Positron emission tomography (PET) scans are vital imaging tools utilized by healthcare professionals, particularly oncologists, to gain detailed insights into lung health. If you’re navigating concerns about lung conditions, especially lung cancer, you might be wondering, “What Is A Pet Scan Of The Lungs and why is it necessary?”. This guide aims to clarify what a PET scan entails, its crucial role in diagnosing and managing lung cancer, and what you can expect throughout the process. PET scans are often employed when lung cancer is suspected, to determine the stage of the disease, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatments. Understanding the procedure can alleviate anxiety and empower you with knowledge about your healthcare journey.
How Does a PET Scan of the Lungs Work?
A PET scan is an advanced imaging technique that provides three-dimensional views inside your body, focusing on metabolic activity at a cellular level. Unlike X-rays or CT scans that primarily show structure, a PET scan reveals how your tissues and organs are functioning. To achieve this, a small amount of radioactive tracer, typically attached to glucose (sugar), is administered into your bloodstream. This tracer is designed to highlight areas with high metabolic activity.
Detecting Lung Issues with Radioactive Tracers
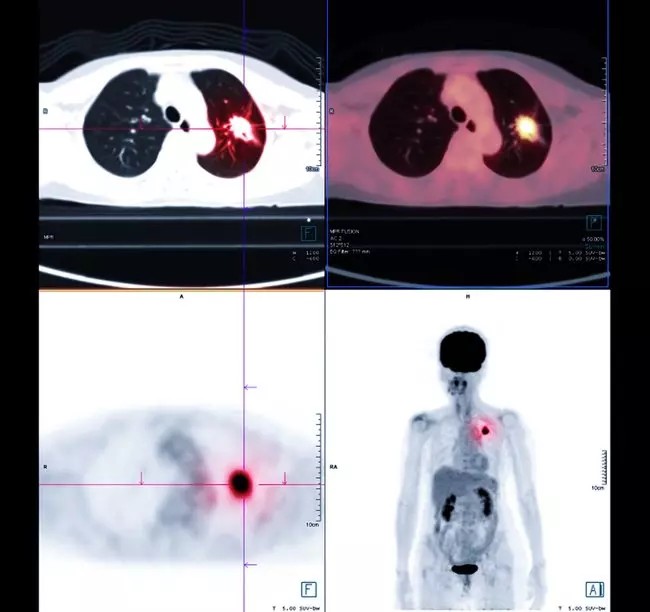
The key to a PET scan’s effectiveness lies in how different cells in your body utilize glucose. Cells that are highly active, such as cancer cells, consume glucose at a much faster rate than normal cells. When the radioactive glucose tracer is injected, these active cells absorb a greater amount of it. The PET scanner then detects the radioactivity emitted by the tracer, pinpointing areas in the lungs with increased glucose uptake. These areas appear as bright spots on the PET scan images, indicating potentially cancerous or highly active tissues.
A PET scan uses radioactive tracers to highlight areas with high metabolic activity in the lungs, which can indicate conditions like cancer. Cells with high metabolic activity are shown in brighter colors like yellow and red.
Often, doctors may order a combined PET-CT scan. This combines the metabolic information from the PET scan with the detailed anatomical images from a computed tomography (CT) scan. The fusion of these two scans provides a more comprehensive view, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, especially in cases like lung cancer where precise location and metabolic activity are critical.
Diagnostic Accuracy of PET Scans for Lung Cancer
PET and PET-CT scans are recognized as highly accurate imaging modalities for assessing lung cancer. They play a crucial role in determining the extent and location of cancer cells before, during, and after treatment. One of the significant advantages of a PET scan is its ability to potentially avoid invasive procedures. For instance, it can often determine if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes without requiring a surgical biopsy. Furthermore, PET scans are valuable in differentiating between benign and malignant lung nodules, aiding in earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Understanding False Positives in Lung PET Scans
While PET scans are highly accurate, it’s important to be aware of the possibility of false-positive results. A false positive occurs when the scan indicates the presence of cancer when, in reality, no cancer is present. This can happen because conditions other than cancer, particularly inflammation due to infections or other diseases, can also cause increased metabolic activity and light up on a PET scan. Studies indicate a false-positive rate of around 6.5 percent. This means that a small percentage of PET scans might suggest lung cancer when another condition is actually responsible for the increased activity.
Understanding False Negatives in Lung PET Scans
Conversely, false-negative results are also a consideration, though less frequent. A false negative occurs when the PET scan fails to detect cancer that is actually present. This is more likely to happen with very small lung nodules, particularly those smaller than 1 centimeter. In such cases, the metabolic activity of the cancer cells might be too low to be detected by the PET scan. When lung cancer diagnosis is uncertain based on a PET scan, additional diagnostic tools are essential. A biopsy, involving the removal of a tissue sample for microscopic examination, is often used to confirm or rule out cancer definitively. Despite these possibilities, PET scans remain a cornerstone of lung cancer imaging, especially when used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods.
When Do Doctors Order Lung PET Scans?
PET scans are utilized at various critical junctures in lung cancer management, from initial diagnosis to monitoring for recurrence.
PET Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
In diagnosing lung cancer, PET scans help doctors identify abnormal growths or tumors in and around the lungs. They are instrumental in evaluating whether a lung nodule or spot is potentially cancerous or related to a benign condition. To establish a definitive diagnosis, PET scans are often used in combination with other diagnostic tests, such as:
- Blood tests
- Bronchoscopy
- Chest X-rays
- CT scans
- MRI scans
These combined approaches ensure a comprehensive evaluation and more accurate diagnosis.
PET Scans for Lung Cancer Staging
Staging is crucial in lung cancer as it determines the extent of the cancer’s spread and influences treatment decisions. PET scans provide valuable information for staging, showing:
- Tumor size
- Number of tumors
- Precise tumor location
- Metastasis – whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs
This detailed information is essential for accurately staging lung cancer, which in turn guides the selection of the most appropriate treatment strategy.
A PET scan can help determine if lung cancer has metastasized, or spread to other parts of the body, by highlighting areas of cancerous activity beyond the lungs.
Guiding Lung Cancer Treatment Plans
PET scan images are invaluable in guiding treatment planning. They can help oncologists pinpoint the optimal site for a biopsy to confirm lung cancer diagnosis. Furthermore, the metabolic activity revealed by PET scans assists doctors in determining the most effective treatment options, tailored to the specific characteristics of the patient’s tumor(s).
Evaluating Lung Cancer Treatment Effectiveness
PET scans are also employed to assess how well lung cancer is responding to treatment. By comparing scans taken before and during treatment, doctors can determine if tumors are shrinking, growing, or remaining stable. While the use of PET scans for treatment evaluation is still a topic of discussion in the medical community, many clinicians find them beneficial, alongside other assessments, in gauging treatment efficacy.
Monitoring Ongoing Lung Cancer Care
Follow-up PET scans can be used to detect lung cancer recurrence. Early detection of recurrent cancer is critical for effective treatment. However, the routine use of PET scans for follow-up is debated, with some healthcare providers weighing the benefits against the cost and radiation exposure from the radioactive tracer.
How To Prepare for a Lung PET Scan
Proper preparation is essential for ensuring the accuracy and success of a lung PET scan. Your healthcare provider will give you detailed instructions, but it’s crucial to inform them if you:
- Have a history of allergic reactions.
- Are currently ill.
- Have diabetes or any chronic health conditions.
- Suspect you might be pregnant.
- Have claustrophobia.
- Are taking any medications, including over-the-counter drugs or supplements.
- Are breastfeeding.
Generally, you will need to fast for several hours before the scan, typically at least four to six hours. You may also be advised to avoid strenuous exercise for about 24 hours prior to the scan.
What To Expect During a Lung PET Scan
On the day of your PET scan, a radioactive tracer will be administered, usually through an intravenous (IV) line. After the injection, you’ll need to wait for approximately one hour to allow your body to absorb the tracer. During this time, you will rest in the radiology or nuclear medicine department.
The PET scanner itself resembles a large, ring-shaped machine. When it’s time for the scan, you will lie down on a platform that slides into the scanner. It’s important to remain as still as possible during the scan, which typically lasts about an hour. The procedure is painless. If you experience anxiety, inform your technician or ask your doctor about relaxation medication beforehand.
During a PET scan, patients lie still on a platform that moves through the scanner. The process is painless and usually takes about an hour to complete.
How Long Does It Take To Get Lung PET Scan Results?
You can generally expect to receive your PET scan results within a few days after the procedure. This waiting period can be emotionally challenging. It’s important to remember that your healthcare team is committed to providing you with the best possible care and that having detailed information from the PET scan is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. If the results are unclear or require further investigation, your doctor may recommend additional tests to ensure the most accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. Don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion on your scan results and proposed next steps to feel confident in your care.
Get Support From Others Who Understand
Navigating lung health concerns can be overwhelming, and connecting with others facing similar experiences can be incredibly helpful. Online communities like MyLungCancerTeam offer a platform to connect with individuals from around the world who understand the challenges of living with lung cancer. These communities provide a space to ask questions, share experiences, and find mutual support.
If you have undergone a PET scan for your lungs, sharing your experience can offer valuable insights and reassurance to others. Consider sharing your tips and experiences within supportive communities to help others navigate their journey.