Are you wondering What Unit Ap World Is Peter The Great in? Peter the Great is typically covered in Unit 3: Land-Based Empires (1450-1750) in AP World History. PETS.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources to help you ace this unit and understand Peter the Great’s impact. Dive in to explore the nuances of his reign and its historical significance!
1. Who Was Peter the Great?
Peter the Great, or Peter I, reigned as Tsar of Russia and later as Emperor of All Russia from 1682 until his death in 1725. He belonged to the Romanov dynasty and is renowned for his efforts to modernize Russia, transforming it into a major European power.
1.1 Early Life and Ascension to the Throne
Peter was born on June 9, 1672, in Moscow. He was the son of Tsar Alexis I and his second wife, Natalya Naryshkina. Due to political intrigues and power struggles, Peter’s early life was tumultuous. After the death of Tsar Alexis, Peter’s older half-brother, Feodor III, briefly ruled. Upon Feodor’s death in 1682, the succession was contested between Peter and his half-brother Ivan.
Ultimately, a compromise was reached where both Peter and Ivan were proclaimed co-Tsars, with their elder sister Sophia acting as regent. Sophia’s regency lasted until 1689, when Peter, with the support of loyal military forces, ousted her and took control of the government. Ivan remained a co-Tsar in name only, with Peter effectively ruling Russia from 1689 onwards.
1.2 Key Policies and Reforms of Peter the Great
Peter the Great implemented extensive reforms aimed at modernizing Russia and transforming it into a major European power. His reforms spanned various aspects of Russian society, including the military, government, economy, and culture.
1.2.1 Military Reforms
One of Peter’s primary goals was to create a modern, efficient army. He reorganized the Russian military along Western European lines, introducing new tactics, training methods, and weaponry. Key military reforms included:
- Establishment of a Regular Army: Peter replaced the old, unreliable streltsy (musketeer corps) with a standing army of professional soldiers recruited from all segments of society.
- Naval Development: Recognizing the importance of naval power, Peter initiated the construction of a Russian navy, establishing shipyards and recruiting foreign experts to train Russian sailors.
- Military Education: Peter established military academies and schools to train officers and specialists, ensuring a steady supply of qualified personnel for the armed forces.
1.2.2 Government Reforms
Peter implemented significant changes to the Russian government to enhance efficiency and centralize authority. Key government reforms included:
- Creation of the Senate: Peter established the Senate as a central administrative body to oversee government affairs in his absence. The Senate was composed of appointed officials responsible for various departments and regions.
- Establishment of Colleges: Peter replaced the old, cumbersome prikaz system with a system of colleges, each responsible for a specific area of government administration, such as foreign affairs, war, and justice.
- Table of Ranks: Peter introduced the Table of Ranks, a system that ranked government officials and military officers based on merit and service rather than noble birth. This allowed talented individuals from lower social classes to rise through the ranks and serve the state.
1.2.3 Economic Reforms
Peter pursued policies aimed at stimulating economic growth and development in Russia. Key economic reforms included:
- Mercantilism: Peter adopted mercantilist policies to promote domestic industries and increase exports while limiting imports.
- Infrastructure Development: Peter invested in infrastructure projects, such as canals, roads, and shipyards, to facilitate trade and transportation.
- Industrial Development: Peter encouraged the establishment of new industries, particularly in mining and metallurgy, to supply the military and reduce Russia’s dependence on foreign imports.
1.2.4 Cultural Reforms
Peter sought to Westernize Russian culture and society, encouraging the adoption of European customs, dress, and education. Key cultural reforms included:
- Adoption of Western Dress: Peter ordered the Russian nobility to adopt Western-style clothing and hairstyles, abandoning traditional Russian attire.
- Promotion of Education: Peter established schools and academies to promote education and literacy, inviting foreign teachers and scholars to Russia.
- Introduction of the Julian Calendar: Peter replaced the old Byzantine calendar with the Julian calendar, bringing Russia in line with Western Europe.
1.3 Impact and Legacy of Peter the Great
Peter the Great’s reforms had a profound and lasting impact on Russia. He transformed Russia into a major European power, modernized its military and government, and stimulated economic and cultural development. However, his reforms also had negative consequences, including increased taxation, forced labor, and social unrest.
Despite these drawbacks, Peter the Great is remembered as one of Russia’s most important and influential rulers. His legacy continues to shape Russian identity and its place in the world.
2. Why Is Peter the Great Important in AP World History?
Peter the Great is a crucial figure in AP World History for several reasons. His reign exemplifies major themes of the period, including state-building, empire expansion, and cultural exchange. Understanding Peter’s reforms and their impact provides valuable insights into the dynamics of early modern Europe and the broader world.
2.1 State-Building and Centralization of Power
Peter the Great’s efforts to modernize Russia and strengthen its military and government reflect broader trends of state-building and centralization of power in early modern Europe. Like other rulers of the period, such as Louis XIV of France and Frederick the Great of Prussia, Peter sought to consolidate his authority and create a more efficient and effective state.
2.2 Empire Expansion and Geopolitical Competition
Peter’s reign was marked by territorial expansion and geopolitical competition with neighboring powers, such as Sweden, the Ottoman Empire, and Poland. His successful military campaigns, including the Great Northern War against Sweden, allowed Russia to gain access to the Baltic Sea and establish itself as a major player in European politics.
2.3 Cultural Exchange and Westernization
Peter the Great’s efforts to Westernize Russian culture and society highlight the increasing interconnectedness of the world in the early modern period. His policies of adopting European customs, dress, and education reflect broader patterns of cultural exchange and influence between Europe and other parts of the world.
3. Key Concepts Related to Peter the Great in AP World History
To fully understand Peter the Great’s significance in AP World History, it’s essential to grasp several key concepts related to his reign and the broader historical context.
3.1 Absolutism
Absolutism refers to a political system in which the ruler holds supreme authority and is not subject to legal or constitutional constraints. Peter the Great is often considered an absolute monarch due to his autocratic rule and efforts to centralize power in his own hands.
3.2 Mercantilism
Mercantilism is an economic theory that emphasizes state intervention in the economy to promote national wealth and power. Peter the Great adopted mercantilist policies to stimulate domestic industries, increase exports, and accumulate wealth for the Russian state.
3.3 Westernization
Westernization refers to the process of adopting Western European ideas, institutions, and culture. Peter the Great’s efforts to modernize Russia involved extensive Westernization, including the adoption of European military tactics, government structures, and cultural practices.
3.4 Modernization
Modernization refers to the process of social, economic, and political transformation that accompanies industrialization and technological advancement. Peter the Great’s reforms aimed to modernize Russia and bring it in line with the more advanced nations of Western Europe.
4. Examining Primary and Secondary Sources on Peter the Great
Delving into primary and secondary sources provides a richer understanding of Peter the Great’s era. Here’s how to approach these sources:
4.1 Primary Sources
Examples of Primary Sources:
- Peter the Great’s Decrees: Official edicts and laws issued by Peter, providing insights into his policies and administrative style.
- Letters and Memoirs: Personal letters from Peter and memoirs from individuals who knew him, offering firsthand accounts of his personality and actions.
- Travel Logs: Records from Peter’s travels abroad, showing his observations and interactions with foreign cultures.
Analyzing Primary Sources:
- Authenticity: Verify the source’s genuineness and origin.
- Context: Understand the historical and social environment in which the source was created.
- Bias: Identify potential biases or perspectives that might influence the source’s portrayal of events.
- Interpretation: Draw conclusions based on the evidence presented in the source.
4.2 Secondary Sources
Examples of Secondary Sources:
- Biographies of Peter the Great: Comprehensive accounts of Peter’s life, achievements, and impact.
- Scholarly Articles: Analyses of specific aspects of Peter’s reign, such as his military reforms or cultural policies.
- Textbooks: General overviews of Peter’s significance in the context of Russian and world history.
Evaluating Secondary Sources:
- Author Credibility: Assess the author’s expertise and qualifications.
- Evidence: Examine the evidence and sources used to support the author’s arguments.
- Perspective: Consider the author’s interpretive framework and potential biases.
- Comparison: Compare different secondary sources to gain a balanced understanding of the topic.
5. Connecting Peter the Great to Other AP World History Topics
Understanding how Peter the Great connects to other topics in AP World History can deepen your comprehension and analytical skills. Here are a few connections to consider:
5.1 The Enlightenment
Peter’s reforms occurred during the Age of Enlightenment, a period of intellectual and cultural ferment in Europe. While Peter was not directly influenced by Enlightenment ideas, his emphasis on reason, progress, and secularism aligns with some of the values of the Enlightenment.
5.2 The French Revolution
The French Revolution, which began in 1789, was partly inspired by Enlightenment ideals of liberty, equality, and popular sovereignty. Peter the Great’s autocratic rule and efforts to modernize Russia can be contrasted with the revolutionary movements that challenged monarchical authority in Europe.
5.3 The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, transformed European economies and societies. Peter the Great’s efforts to promote economic development in Russia can be seen as a precursor to the industrialization that would later sweep across Europe and the world.
6. DBQ and Essay Topics on Peter the Great
Peter the Great is a popular topic for Document-Based Questions (DBQs) and essays on the AP World History exam. Here are some potential DBQ and essay topics to consider:
6.1 DBQ Topics
- Analyze the extent to which Peter the Great’s reforms transformed Russian society in the 18th century.
- Evaluate the similarities and differences between Peter the Great’s modernization efforts and those of other rulers in early modern Europe.
- Assess the impact of Peter the Great’s military reforms on Russia’s foreign policy and geopolitical position.
6.2 Essay Topics
- To what extent was Peter the Great an enlightened despot?
- Compare and contrast the motivations and methods of Peter the Great and Catherine the Great in their efforts to modernize Russia.
- Analyze the long-term consequences of Peter the Great’s reforms on Russian society, politics, and culture.
7. Peter the Great’s Impact on Russian Society and Culture
Peter the Great’s influence extended beyond political and military reforms, deeply affecting Russian society and culture.
7.1 Social Changes
- Nobility Transformation: Peter mandated that nobles serve in the military or civil administration, tying their status to state service. He also promoted education among the nobility, establishing schools and academies to train them in Western knowledge and skills.
- Changes in Social Customs: Peter introduced Western customs and etiquette, such as requiring men to shave their beards and wear Western-style clothing. He also encouraged social gatherings and parties, promoting interaction between men and women in a more relaxed and informal setting.
- Impact on the Peasantry: While Peter’s reforms primarily targeted the nobility and urban populations, they also had an impact on the peasantry. Increased taxation and labor demands placed a heavy burden on the peasantry, leading to social unrest and rebellion.
7.2 Cultural Transformations
- Adoption of Western Culture: Peter sought to replace traditional Russian culture with Western European culture. He encouraged the adoption of Western art, music, literature, and architecture, inviting foreign artists and architects to Russia to introduce new styles and techniques.
- Establishment of St. Petersburg: Peter founded the city of St. Petersburg as a new capital for Russia, designed to be a modern, European-style city. St. Petersburg became a symbol of Peter’s Westernizing reforms and a center of cultural exchange between Russia and Europe.
- Changes in the Russian Language: Peter introduced Western loanwords into the Russian language, reflecting the growing influence of Western culture on Russian society.
8. Peter the Great’s Foreign Policy and Military Campaigns
Peter the Great’s foreign policy was driven by the desire to secure Russia’s borders, gain access to warm-water ports, and establish Russia as a major European power.
8.1 Key Foreign Policy Objectives
- Access to Warm-Water Ports: Peter sought to gain access to the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea, which would provide Russia with year-round ports for trade and naval operations.
- Territorial Expansion: Peter aimed to expand Russia’s territory through military conquest and diplomatic negotiations.
- European Recognition: Peter sought to gain recognition and respect from other European powers, establishing Russia as an equal player in European politics.
8.2 Major Military Campaigns
- The Great Northern War (1700-1721): This conflict pitted Russia against Sweden, the dominant power in the Baltic region. Peter’s victory in the Great Northern War secured Russia’s access to the Baltic Sea and established it as a major power in Northern Europe.
- The Russo-Ottoman War (1695-1696): Peter launched military campaigns against the Ottoman Empire in an effort to gain access to the Black Sea. Although these campaigns were not entirely successful, they laid the groundwork for future Russian expansion in the region.
- The Persian Campaign (1722-1723): Peter launched a military campaign against Persia, seeking to expand Russian influence in the Caspian Sea region. This campaign resulted in Russia gaining control of several coastal territories.
8.3 Impact on Russia’s Geopolitical Position
Peter the Great’s foreign policy and military campaigns had a profound impact on Russia’s geopolitical position. He transformed Russia from a relatively isolated and backward country into a major European power with access to vital trade routes and a strong military.
9. Peter the Great and the Orthodox Church
Peter the Great’s relationship with the Russian Orthodox Church was complex and often strained. He sought to bring the church under state control and use it as a tool to promote his modernization agenda.
9.1 Church Reforms
- Abolition of the Patriarchate: In 1721, Peter abolished the position of Patriarch, the head of the Russian Orthodox Church, and replaced it with a Holy Synod, a government body that administered church affairs.
- State Control of Church Finances: Peter brought church finances under state control, using church revenues to fund his military and modernization projects.
- Suppression of Religious Dissent: Peter cracked down on religious dissenters, such as the Old Believers, who opposed his reforms and challenged the authority of the state.
9.2 Reasons for Church Reforms
- Control: To exert greater control over the church and prevent it from challenging his authority.
- Resources: To access church wealth and use it to fund his modernization efforts.
- Alignment: To align the church with his Westernizing reforms and promote a more secular worldview.
9.3 Consequences of Church Reforms
- Subordination of the Church: The church became subordinate to the state, losing its independence and autonomy.
- Weakening of Religious Authority: The authority and prestige of the church declined, as it became seen as a tool of the state rather than an independent spiritual institution.
- Increased Secularization: Peter’s reforms contributed to the secularization of Russian society, as traditional religious values were challenged by Western ideas and practices.
10. Common Misconceptions About Peter the Great
There are several common misconceptions about Peter the Great that students should be aware of:
10.1 Misconception 1: Peter the Great Was Solely Responsible for Modernizing Russia
While Peter the Great played a crucial role in modernizing Russia, he was not solely responsible for this process. Other rulers, such as Ivan the Terrible and Alexis I, had also implemented reforms and introduced Western ideas to Russia.
10.2 Misconception 2: Peter the Great’s Reforms Were Universally Welcomed by the Russian People
Peter the Great’s reforms were not universally welcomed by the Russian people. Many Russians, particularly among the peasantry and the Old Believers, opposed his reforms and resisted his efforts to Westernize Russian society.
10.3 Misconception 3: Peter the Great Was a Staunch Supporter of Enlightenment Ideals
While Peter the Great’s reforms aligned with some of the values of the Enlightenment, he was not a staunch supporter of Enlightenment ideals. He was primarily motivated by pragmatic considerations of state power and military effectiveness rather than abstract philosophical principles.
10.4 Misconception 4: Peter the Great Completely Transformed Russian Society
While Peter the Great’s reforms had a profound impact on Russian society, they did not completely transform it. Traditional social structures, cultural practices, and religious beliefs persisted alongside the new Western-inspired institutions and customs.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Peter the Great
Here are some frequently asked questions about Peter the Great:
1. What Were Peter the Great’s Main Goals?
Peter the Great aimed to modernize Russia, expand its territory, gain access to warm-water ports, and establish it as a major European power.
2. What Were Peter the Great’s Most Important Reforms?
Peter the Great’s most important reforms included military reforms, government reforms, economic reforms, and cultural reforms.
3. How Did Peter the Great Westernize Russia?
Peter the Great Westernized Russia by adopting European customs, dress, education, and institutions.
4. What Was the Significance of the Great Northern War?
The Great Northern War secured Russia’s access to the Baltic Sea and established it as a major power in Northern Europe.
5. What Was Peter the Great’s Relationship with the Russian Orthodox Church?
Peter the Great brought the Russian Orthodox Church under state control, abolishing the Patriarchate and using church revenues to fund his modernization projects.
6. How Did Peter the Great’s Reforms Affect Russian Society?
Peter the Great’s reforms transformed Russian society by modernizing its military and government, stimulating economic and cultural development, and increasing state control over various aspects of life.
7. Was Peter the Great an Absolute Monarch?
Yes, Peter the Great is considered an absolute monarch due to his autocratic rule and efforts to centralize power in his own hands.
8. What Was Peter the Great’s Legacy?
Peter the Great’s legacy includes the modernization of Russia, its rise as a major European power, and the establishment of St. Petersburg as a new capital.
9. How Did Peter the Great Impact the Nobility?
Peter mandated state service for nobles, promoted education, and introduced Western customs, transforming their role and culture.
10. How Did Peter the Great’s Policies Affect the Peasantry?
Peter’s policies increased taxation and labor demands on the peasantry, leading to social unrest.
Conclusion: Mastering Peter the Great for AP World History
Understanding Peter the Great is essential for success in AP World History. His reforms, foreign policy, and impact on Russian society and culture provide valuable insights into the dynamics of early modern Europe and the broader world. By studying primary and secondary sources, connecting Peter to other AP World History topics, and addressing common misconceptions, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of this important historical figure.
For more in-depth analysis, resources, and expert guidance on Peter the Great and other AP World History topics, visit PETS.EDU.VN today.
Are you struggling to keep up with your pet’s health needs? PETS.EDU.VN is here to help! Our website offers a wealth of information on pet care, including detailed guides on nutrition, health, and behavior. For instance, learn how to identify and manage common health issues in dogs with our comprehensive guide on dog health.
We understand that finding reliable pet care services can be challenging. That’s why PETS.EDU.VN provides a directory of trusted veterinarians, groomers, and pet sitters in your area. Whether you need a routine check-up or specialized care, our listings make it easy to find the right provider for your furry friend.
Worried about your pet’s behavior? Our expert articles offer practical tips and advice on training and socialization. For example, discover effective techniques for housebreaking your puppy or managing separation anxiety in your cat.
At PETS.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing pet owners with the knowledge and resources they need to ensure their pets live happy, healthy lives. Visit our website today to explore our extensive collection of articles, guides, and service listings.
Address: 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States
WhatsApp: +1 555-987-6543
Website: pets.edu.vn
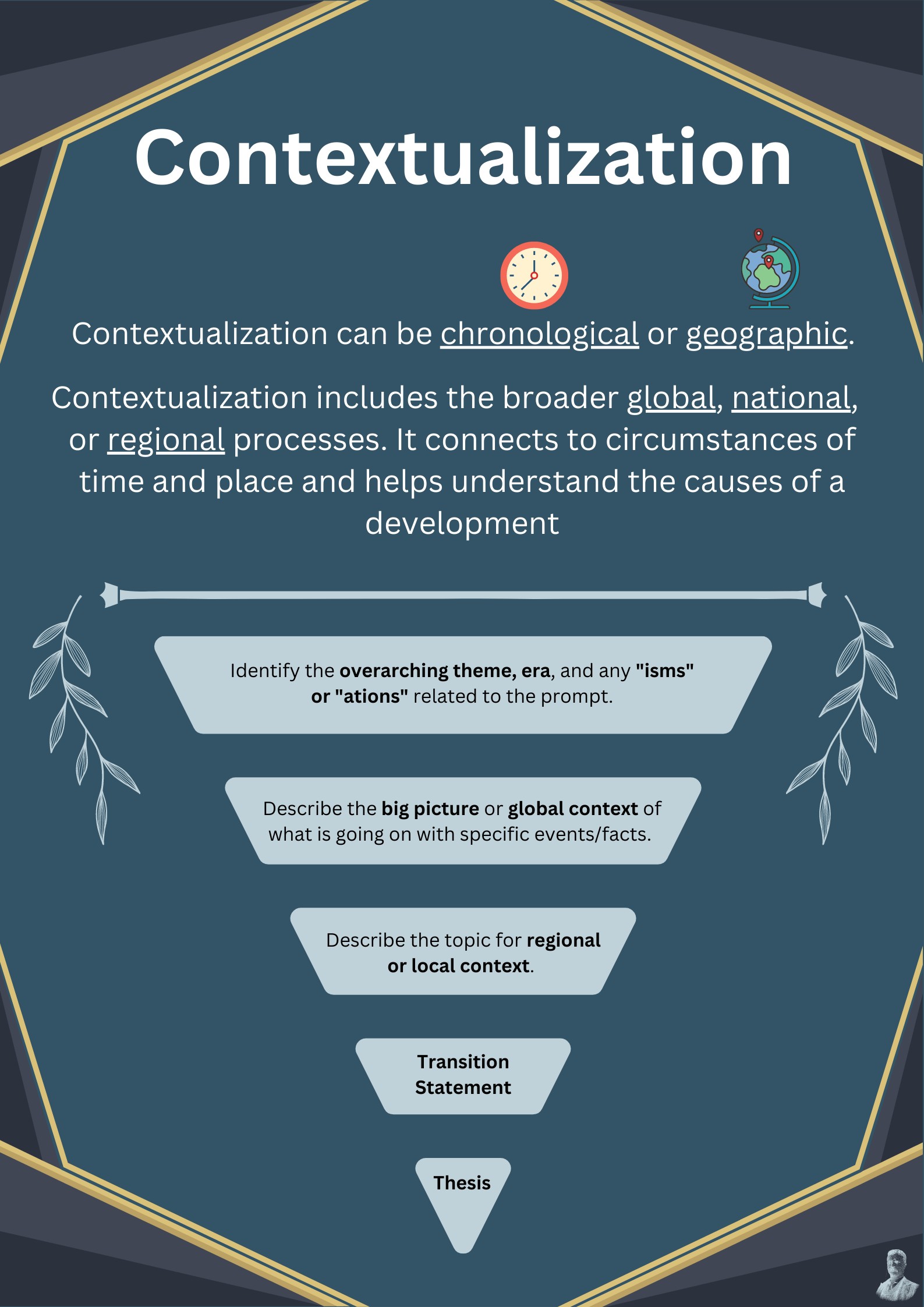
Contextualization is vital for understanding historical figures like Peter the Great.
Primary sources are essential to deeply understand historical events such as the Silk Road trade.