Do Pet Microchips Have Gps capabilities for real-time tracking? Pet microchips utilize Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) to store your contact information, not GPS, but don’t worry! At PETS.EDU.VN, we explain the difference and explore modern GPS pet trackers as an additional safety measure to keep tabs on your beloved animal. Learn how both technologies work together to safeguard your furry friends with detailed information and resources.
1. Understanding Pet Microchips: What They Are and How They Work
Microchips have become an indispensable tool for pet owners, offering a reliable means of identification should your pet ever become lost. But what exactly is a microchip, and how does it work? Let’s delve into the details.
1.1 What is a Pet Microchip?
A pet microchip is a small, electronic device about the size of a grain of rice. It is implanted under your pet’s skin, typically between the shoulder blades. This microchip contains a unique identification number that can be scanned by veterinarians, animal shelters, and animal control officers.
1.2 How Microchips Work
Unlike GPS trackers, microchips do not actively transmit location data. Instead, they operate using Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. Here’s how it works:
- Implantation: A vet injects the microchip under the loose skin between your pet’s shoulder blades. The process is quick and causes minimal discomfort, akin to a routine vaccination.
- Activation: When a scanner is passed over the area, the microchip is activated by the radio waves emitted by the scanner.
- Information Retrieval: The microchip transmits the unique identification number to the scanner.
- Database Lookup: The vet or shelter then uses this number to search a microchip registry database, which contains your contact information associated with the microchip number.
- Reunification: If your contact information is up-to-date, you will be contacted, and arrangements will be made to reunite you with your pet.
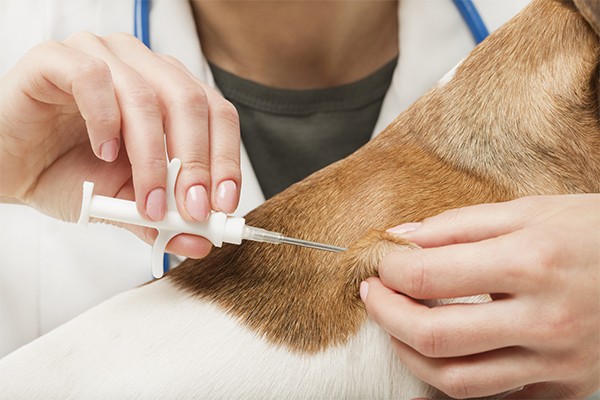 A vet carefully implants a microchip into a dog's shoulder, ensuring proper placement for effective identification.
A vet carefully implants a microchip into a dog's shoulder, ensuring proper placement for effective identification.
1.3 Key Benefits of Microchipping
- Permanent Identification: Unlike collars and tags, microchips cannot be easily removed.
- Increased Recovery Rate: Microchipped pets are much more likely to be returned to their owners.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your pet has a permanent form of identification provides peace of mind.
1.4 Important Considerations
- Registration is Key: The microchip is only effective if you register it with your current contact information.
- Keep Information Updated: If you move or change your phone number, update your registration information immediately.
- Check the Chip Regularly: During your pet’s annual vet visit, ask the vet to scan the microchip to ensure it is still functioning correctly.
Microchipping is a simple yet crucial step in ensuring your pet’s safety. At PETS.EDU.VN, we strongly advocate for microchipping as a fundamental part of responsible pet ownership.
2. Do Pet Microchips Have GPS? The Truth About Tracking Capabilities
One of the most common misconceptions about pet microchips is that they function as GPS trackers. Many pet owners wonder, “Do pet microchips have GPS?” The answer is no. Pet microchips use RFID technology, which is different from GPS.
2.1 RFID vs. GPS: Understanding the Difference
To understand why microchips don’t have GPS, it’s essential to know the difference between RFID and GPS technologies.
| Feature | RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) | GPS (Global Positioning System) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses radio waves to transmit information when scanned | Uses a network of satellites to determine precise location |
| Power Source | Passive; activated by the scanner’s radio waves | Requires a power source (battery) to actively transmit location data |
| Tracking Capability | No real-time tracking; provides identification information when scanned | Provides real-time tracking and location history |
| Size | Very small; about the size of a grain of rice | Larger due to battery and GPS components |
| Cost | Relatively inexpensive | More expensive due to advanced technology and subscription fees |
| Use Cases | Pet identification, inventory management, access control | Navigation, fitness tracking, pet tracking |
| Limitations | Requires close proximity to a scanner; no continuous location updates | Requires a clear line of sight to satellites; battery life can be limited |
2.2 Why Microchips Use RFID Instead of GPS
There are several reasons why microchips rely on RFID technology rather than GPS:
- Size Constraints: GPS technology requires a battery and additional components that would make the microchip too large for implantation.
- Power Requirements: GPS trackers need a continuous power source to transmit location data, which is impractical for a microchip designed to remain dormant until scanned.
- Cost: GPS technology is significantly more expensive than RFID, making it less feasible for widespread use in microchips.
2.3 The Role of Microchips in Pet Recovery
While microchips don’t offer real-time tracking, they play a crucial role in reuniting lost pets with their owners. When a lost pet is found and taken to a vet or shelter, scanning the microchip allows access to the owner’s contact information. This simple yet effective method has reunited countless pets with their families.
2.4 Enhancing Pet Safety with GPS Trackers
For pet owners seeking real-time tracking capabilities, GPS pet trackers are a viable option. These devices attach to your pet’s collar and use satellite technology to pinpoint their location. While they come with additional costs and require regular charging, GPS trackers provide an extra layer of security and peace of mind.
Understanding the difference between RFID microchips and GPS trackers is essential for making informed decisions about your pet’s safety. At PETS.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive resources on both technologies to help you choose the best solution for your needs.
3. Exploring GPS Pet Trackers: Features, Benefits, and Considerations
While pet microchips do not have GPS capabilities, GPS pet trackers are a popular alternative for owners seeking real-time location monitoring. These devices offer advanced features and benefits but also come with certain considerations.
3.1 How GPS Pet Trackers Work
GPS pet trackers use the Global Positioning System (GPS) to determine your pet’s location. Here’s a breakdown of how they work:
- Satellite Connection: The tracker communicates with GPS satellites to determine its precise coordinates.
- Data Transmission: The tracker transmits this location data to your smartphone or computer via cellular networks or radio frequencies.
- Real-Time Monitoring: You can view your pet’s location in real-time through a mobile app or web platform.
- Geofencing: Many GPS trackers allow you to set up virtual boundaries (geofences). If your pet wanders outside these boundaries, you’ll receive an alert.
3.2 Key Features of GPS Pet Trackers
- Real-Time Tracking: Track your pet’s movements in real-time, ensuring you always know their location.
- Geofencing: Create virtual boundaries and receive alerts when your pet leaves designated safe zones.
- Activity Monitoring: Some trackers monitor your pet’s activity levels, providing insights into their daily exercise and behavior.
- Historical Data: Review your pet’s location history to see where they’ve been.
- Alerts and Notifications: Receive alerts for various events, such as low battery, leaving a geofence, or unusual activity.
3.3 Benefits of Using GPS Pet Trackers
- Enhanced Security: GPS trackers provide an extra layer of security, especially for pets prone to wandering.
- Quick Recovery: In the event your pet gets lost, you can quickly locate them using the tracker’s real-time location data.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you can track your pet’s whereabouts at any time offers peace of mind.
- Activity Insights: Activity monitoring features can help you ensure your pet gets enough exercise and identify potential health issues.
3.4 Considerations When Choosing a GPS Pet Tracker
- Size and Weight: Choose a tracker that is appropriately sized for your pet to ensure comfort and mobility.
- Battery Life: Consider the tracker’s battery life and how frequently it needs to be charged.
- Subscription Fees: Many GPS trackers require a monthly subscription fee for cellular connectivity and data services.
- Coverage Area: Ensure the tracker has adequate coverage in your area.
- Durability: Look for a tracker that is durable and water-resistant to withstand outdoor conditions.
3.5 Top GPS Pet Trackers on the Market
| Tracker | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tractive GPS Dog Tracker | Real-time tracking, geofencing, activity monitoring, unlimited range | Accurate tracking, easy to use, durable, good battery life, affordable subscription plans | Requires a subscription, some users report occasional connectivity issues |
| Whistle Go Explore | GPS tracking, activity monitoring, health insights, geofencing, long battery life | Comprehensive health and activity monitoring, reliable tracking, user-friendly app, extended battery life | Higher subscription cost compared to some competitors, larger size may not be suitable for small pets |
| Fi Smart Dog Collar | GPS tracking, activity monitoring, lost dog mode, LED safety light, durable design | Stylish design, accurate tracking, long battery life, useful safety features, strong and durable | More expensive than other options, subscription required |
| Garmin Astro 900 | GPS and GLONASS tracking, long-range tracking, detailed mapping, durable and waterproof | Excellent for hunting dogs and rural areas, long-range tracking capabilities, rugged and reliable, no subscription required | Expensive upfront cost, bulkier design, may not be suitable for urban environments |
| Apple AirTag | Bluetooth tracking, integration with Apple ecosystem, lost mode with notifications | Affordable, easy to set up, integrates seamlessly with Apple devices, large network of users to help locate lost pets | Limited range (Bluetooth only), requires other Apple devices nearby to update location, not specifically designed for pets, no geofencing |
By carefully evaluating these factors and exploring available options, you can choose a GPS pet tracker that meets your specific needs and provides the best possible protection for your furry friend. At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide detailed reviews and comparisons of various GPS pet trackers to help you make an informed decision.
4. Microchipping vs. GPS Tracking: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding the distinct roles of microchips and GPS trackers is crucial for comprehensive pet protection. While microchips offer permanent identification, GPS trackers provide real-time location monitoring. Let’s compare these two technologies to help you make the best choice for your pet’s safety.
4.1 Key Differences
| Feature | Microchip | GPS Tracker |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) | GPS (Global Positioning System) |
| Tracking | No real-time tracking | Real-time tracking and location history |
| Power | Passive; activated by scanner | Requires battery power |
| Size | Tiny; about the size of a grain of rice | Larger; attaches to collar |
| Cost | One-time fee for implantation | Ongoing costs (device + subscription) |
| Function | Identification; provides contact information when scanned | Location monitoring; provides real-time location data |
| Use Cases | Permanent ID, reunification with lost pets | Tracking wandering pets, geofencing, activity monitoring |
| Limitations | Requires scanning; no active tracking | Requires charging, subscription fees, limited battery life, coverage issues |
4.2 When to Use a Microchip
- Essential for All Pets: Microchipping is a fundamental part of responsible pet ownership and is recommended for all pets.
- Permanent Identification: Microchips provide a permanent form of identification that cannot be removed or lost.
- Legal Requirement: Many regions require pets to be microchipped by law.
4.3 When to Use a GPS Tracker
- Wandering Pets: If your pet has a history of wandering or escaping, a GPS tracker can provide peace of mind.
- Outdoor Activities: For pets that enjoy outdoor activities like hiking or camping, a GPS tracker can help you keep track of their location.
- Anxiety Relief: GPS trackers can alleviate anxiety for owners of pets with separation anxiety or those prone to getting lost.
4.4 Combining Microchips and GPS Trackers for Optimal Protection
The most effective approach to pet safety is to combine microchipping with GPS tracking. Here’s why:
- Redundancy: Microchips provide a backup form of identification if the GPS tracker fails or is lost.
- Comprehensive Protection: Together, they offer both permanent identification and real-time location monitoring.
- Increased Recovery Rate: The combination of technologies significantly increases the chances of reuniting with your pet if they get lost.
4.5 Expert Recommendations
Veterinarians and pet safety experts recommend microchipping all pets and considering GPS trackers for pets at higher risk of getting lost. According to the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), microchipped pets are significantly more likely to be returned to their owners.
4.6 Making an Informed Decision
Choosing between microchips and GPS trackers depends on your pet’s individual needs and your personal preferences. At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide detailed information and expert advice to help you make an informed decision. Consider your pet’s behavior, lifestyle, and risk factors when selecting the right combination of technologies for their safety.
5. How to Register and Update Your Pet’s Microchip Information
Registering your pet’s microchip is a critical step in ensuring their safe return if they ever get lost. Without accurate registration information, the microchip is essentially useless. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to register and update your pet’s microchip information.
5.1 Why Registration is Essential
Microchips store a unique identification number, but this number is only useful if it’s linked to your contact information in a microchip registry. When a lost pet is found and scanned, the registry is used to look up the owner’s information. If your contact details are missing or outdated, you may not be reunited with your pet.
5.2 Steps to Register Your Pet’s Microchip
- Identify the Microchip Provider: Determine which company manufactured your pet’s microchip. This information is usually provided by your veterinarian or on the microchip paperwork.
- Visit the Provider’s Website: Go to the microchip provider’s website and look for the registration section.
- Create an Account: Create an account on the provider’s website, if you don’t already have one.
- Enter the Microchip Number: Enter your pet’s microchip number and follow the instructions to add your contact information.
- Pay the Registration Fee: Some registries charge a one-time or annual fee for registration. Be prepared to pay this fee to complete the process.
- Verify Your Information: Double-check all the information you’ve entered to ensure it is accurate.
5.3 Popular Microchip Registries
- PetLink: One of the largest microchip registries in North America.
- AKC Reunite: The official microchip registry of the American Kennel Club.
- HomeAgain: A popular microchip registry with advanced features and services.
- Found Animals Registry: A free, non-profit microchip registry.
5.4 How to Update Your Microchip Information
It’s essential to keep your microchip information up-to-date, especially if you move, change your phone number, or change your email address. Here’s how to update your information:
- Log into Your Account: Log into your account on the microchip registry website.
- Find the Update Section: Look for the section that allows you to update your contact information.
- Enter Your New Information: Enter your new address, phone number, and email address.
- Save Your Changes: Save your changes and verify that the updated information is correct.
5.5 Best Practices for Microchip Registration
- Register Immediately: Register your pet’s microchip as soon as possible after implantation.
- Use a Reliable Registry: Choose a reputable microchip registry with a proven track record.
- Keep Records: Keep a copy of your pet’s microchip number and registration information in a safe place.
- Update Regularly: Review and update your contact information at least once a year, or whenever your information changes.
- Consider Multiple Registries: Registering your pet’s microchip with multiple registries can increase the chances of reunification.
5.6 The Importance of Keeping Information Current
Failing to update your microchip information can have serious consequences. According to a study by the American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA), pets with outdated microchip information are much less likely to be returned to their owners.
By following these steps and best practices, you can ensure that your pet’s microchip is properly registered and that your contact information is always up-to-date. At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide resources and support to help you navigate the microchip registration process and keep your pet safe.
6. Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions About Pet Microchips
Pet microchips are a valuable tool for pet identification, but they are often misunderstood. Addressing common concerns and misconceptions can help pet owners make informed decisions about microchipping their beloved animals.
6.1 “Microchips Can Track My Pet’s Location.”
Reality: Microchips do not have GPS capabilities and cannot track your pet’s location in real-time. They use RFID technology, which only provides identification information when scanned.
6.2 “Microchipping is Painful for My Pet.”
Reality: Microchipping is a quick and relatively painless procedure. Most pets experience only minimal discomfort, similar to a routine vaccination.
6.3 “Microchips Can Cause Cancer in Pets.”
Reality: The risk of microchip-related cancer is extremely low. Studies have shown that the incidence of microchip-associated tumors is very rare.
6.4 “My Pet Always Wears a Collar with ID Tags, So a Microchip is Unnecessary.”
Reality: Collars and ID tags can be lost or removed, while a microchip is a permanent form of identification that cannot be lost. It’s best to have both for optimal protection.
6.5 “Registering My Pet’s Microchip is Too Complicated.”
Reality: Registering a microchip is a simple process that can be completed online in a matter of minutes. Most microchip registries offer user-friendly interfaces and clear instructions.
6.6 “Microchips Can Store My Pet’s Medical Records.”
Reality: Microchips only store a unique identification number and your contact information. They cannot store medical records or other personal information.
6.7 “Microchips Are Only Necessary for Dogs and Cats.”
Reality: Microchips can be used for a variety of pets, including dogs, cats, rabbits, birds, and even horses. Any pet that could potentially get lost can benefit from microchipping.
6.8 “Microchips Last Forever and Never Need to Be Checked.”
Reality: While microchips are designed to last for the life of your pet, it’s a good idea to have your veterinarian scan the microchip during annual check-ups to ensure it is still functioning properly.
6.9 “All Microchip Scanners Can Read All Microchips.”
Reality: While most microchip scanners can read a variety of microchip frequencies, there are some older scanners that may not be compatible with newer microchips. It’s important to ensure that your veterinarian or local shelter has a universal scanner.
6.10 “Microchipping Guarantees That I Will Get My Pet Back If They Get Lost.”
Reality: While microchipping significantly increases the chances of reuniting with your lost pet, it’s not a guarantee. You must keep your contact information up-to-date and ensure that the microchip is registered with a reputable registry.
By addressing these common concerns and misconceptions, pet owners can better understand the benefits and limitations of microchips. At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide accurate and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your pet’s health and safety.
7. Alternative Pet Identification Methods: Collars, Tags, and More
While microchips are a permanent form of identification, and GPS trackers offer real-time location monitoring, other pet identification methods can also play a role in ensuring your pet’s safety. Collars, tags, and other methods can complement microchipping and GPS tracking to provide comprehensive protection.
7.1 Collars and ID Tags
- Visibility: Collars and ID tags are immediately visible and can quickly provide information to anyone who finds your pet.
- Essential Information: ID tags should include your pet’s name, your phone number, and any important medical information.
- Durability: Choose a durable collar and tag that can withstand outdoor conditions.
- Legality: Many regions require pets to wear collars with ID tags by law.
7.2 Temporary Tattoos
- Temporary Identification: Temporary tattoos can be used to provide temporary identification, such as during travel or events.
- Contact Information: These tattoos can include your phone number or other contact information.
- Non-Invasive: Temporary tattoos are non-invasive and easy to apply.
7.3 Social Media Pet Groups
- Local Networks: Social media pet groups can be a valuable resource for finding lost pets in your local area.
- Community Support: These groups allow you to post photos and information about your lost pet and receive support from the community.
- Rapid Dissemination: Social media can quickly spread the word about your lost pet.
7.4 Pet Amber Alert Systems
- Emergency Alerts: Pet Amber Alert systems send out alerts to local pet owners and shelters when a pet goes missing.
- Wide Reach: These systems can quickly reach a large number of people in your area.
- Community Collaboration: Pet Amber Alert systems rely on community collaboration to help find lost pets.
7.5 Nose Printing
- Unique Identification: A pet’s nose print is as unique as a human fingerprint.
- Permanent Record: Nose prints can be used to create a permanent record of your pet’s identity.
- Forensic Use: Nose prints can be used in forensic investigations to identify lost or stolen pets.
7.6 The Importance of Multiple Identification Methods
Using multiple identification methods can significantly increase the chances of reuniting with your lost pet. Microchips provide permanent identification, GPS trackers offer real-time location monitoring, and collars and tags provide visible information.
7.7 Expert Recommendations
Pet safety experts recommend using a combination of identification methods to ensure comprehensive protection for your pet. According to the National Animal Care & Control Association (NACA), pets with multiple forms of identification are more likely to be returned to their owners.
7.8 Making an Informed Decision
Choosing the right combination of identification methods depends on your pet’s individual needs and your personal preferences. At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide detailed information and expert advice to help you make an informed decision. Consider your pet’s behavior, lifestyle, and risk factors when selecting the right identification methods for their safety.
8. Legal and Ethical Considerations of Pet Tracking
As pet tracking technology becomes more advanced, it’s important to consider the legal and ethical implications of using these devices. Understanding the laws and ethical principles surrounding pet tracking can help you make responsible decisions about monitoring your pet’s location.
8.1 Privacy Concerns
- Data Security: GPS trackers collect and transmit data about your pet’s location, raising concerns about data security and privacy.
- Unauthorized Access: It’s important to choose a GPS tracker with robust security features to prevent unauthorized access to your pet’s location data.
- Data Storage: Be aware of how long your pet’s location data is stored and how it is used by the tracker provider.
8.2 Legal Regulations
- Local Laws: Check local laws and regulations regarding pet tracking, as some areas may have restrictions on the use of GPS trackers.
- Privacy Laws: Be aware of privacy laws that may apply to the collection and use of your pet’s location data.
- Trespassing Laws: Ensure that your pet is not trespassing on private property while being tracked.
8.3 Ethical Considerations
- Invasion of Privacy: Consider whether tracking your pet’s location is an invasion of their privacy.
- Freedom to Roam: Balance the benefits of tracking with your pet’s freedom to roam and explore their environment.
- Responsible Use: Use pet tracking technology responsibly and ethically, respecting your pet’s rights and well-being.
8.4 Microchip Laws
- Mandatory Microchipping: Many regions have laws requiring pets to be microchipped.
- Registration Requirements: Some laws require pet owners to register their pet’s microchip with a national registry.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with microchip laws can result in fines or other penalties.
8.5 Best Practices for Ethical Pet Tracking
- Informed Consent: If possible, involve your pet in the decision-making process by observing their reaction to the tracking device.
- Transparency: Be transparent about your use of pet tracking technology with anyone who cares for your pet.
- Data Security: Choose a GPS tracker with strong data security features to protect your pet’s location data.
- Responsible Use: Use pet tracking technology responsibly and ethically, respecting your pet’s rights and well-being.
8.6 Expert Recommendations
Animal welfare organizations and legal experts recommend considering the legal and ethical implications of pet tracking before using these devices. According to the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA), pet owners should use tracking technology responsibly and ethically, respecting their pet’s rights and well-being.
8.7 Making an Informed Decision
Understanding the legal and ethical considerations of pet tracking can help you make responsible decisions about monitoring your pet’s location. At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide detailed information and expert advice to help you navigate these complex issues. Consider the privacy, legal, and ethical implications of pet tracking when selecting the right technology for your pet’s safety.
9. Future Trends in Pet Tracking Technology
Pet tracking technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and advancements emerging regularly. Staying informed about future trends in pet tracking can help you make informed decisions about protecting your pet and staying ahead of the curve.
9.1 Improved GPS Accuracy
- Advanced Algorithms: Future GPS trackers will likely use more advanced algorithms to improve location accuracy.
- Satellite Technology: New satellite technology will provide more precise and reliable location data.
- Real-Time Updates: Expect faster and more frequent location updates for real-time tracking.
9.2 Enhanced Battery Life
- Energy-Efficient Designs: Future GPS trackers will be designed to be more energy-efficient, extending battery life.
- Wireless Charging: Wireless charging capabilities will make it easier to keep your pet’s tracker powered up.
- Solar-Powered Trackers: Solar-powered trackers will provide a sustainable and long-lasting power source.
9.3 Integration with Smart Home Devices
- Smart Home Connectivity: Future pet trackers will integrate with smart home devices, allowing you to monitor your pet’s location from anywhere.
- Automated Alerts: Smart home integration will enable automated alerts and notifications based on your pet’s location.
- Remote Monitoring: You’ll be able to remotely monitor your pet’s location and activity through your smart home system.
9.4 Health Monitoring Capabilities
- Activity Tracking: Future pet trackers will offer more advanced activity tracking capabilities, monitoring your pet’s exercise levels and sleep patterns.
- Vital Sign Monitoring: Some trackers may be able to monitor your pet’s vital signs, such as heart rate and body temperature.
- Early Detection of Illness: Health monitoring features could help detect early signs of illness or injury.
9.5 Smaller and Lighter Designs
- Miniaturization: Future pet trackers will be smaller and lighter, making them more comfortable for pets to wear.
- Ergonomic Designs: Ergonomic designs will ensure that trackers fit securely and don’t interfere with your pet’s movement.
- Improved Comfort: Smaller and lighter trackers will improve your pet’s comfort and reduce the risk of irritation or injury.
9.6 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
- AI-Powered Insights: AI algorithms will analyze your pet’s location and activity data to provide valuable insights into their behavior and health.
- Predictive Analytics: AI could predict potential health issues or behavioral problems based on your pet’s data.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI-powered trackers could offer personalized recommendations for improving your pet’s health and well-being.
9.7 Expert Predictions
Technology experts predict that pet tracking technology will become more sophisticated and integrated into our daily lives in the coming years. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global pet tracking market is expected to grow significantly in the next decade, driven by increasing pet ownership and advancements in technology.
9.8 Staying Informed
Staying informed about future trends in pet tracking technology can help you make informed decisions about protecting your pet and staying ahead of the curve. At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide the latest news, reviews, and insights on pet tracking technology to keep you informed and empowered.
10. Conclusion: Ensuring Your Pet’s Safety with Microchips and GPS Trackers
Ensuring your pet’s safety is a top priority for any responsible pet owner. While the question “Do pet microchips have GPS?” is answered with a no, understanding the roles of both microchips and GPS trackers is crucial for comprehensive pet protection. Microchips provide permanent identification, while GPS trackers offer real-time location monitoring.
10.1 Key Takeaways
- Microchips Use RFID: Pet microchips use RFID technology and do not have GPS capabilities.
- GPS Trackers Offer Real-Time Tracking: GPS pet trackers use satellite technology to provide real-time location monitoring.
- Registration is Essential: Registering your pet’s microchip is crucial for ensuring their safe return if they get lost.
- Update Your Information: Keep your microchip information up-to-date, especially if you move or change your contact details.
- Consider GPS Trackers for Wandering Pets: GPS trackers can provide peace of mind for owners of pets prone to wandering.
- Combine Microchips and GPS Trackers: The most effective approach to pet safety is to combine microchipping with GPS tracking.
- Stay Informed About Future Trends: Staying informed about future trends in pet tracking technology can help you make informed decisions.
10.2 The Importance of Proactive Pet Protection
Proactive pet protection involves taking steps to prevent your pet from getting lost in the first place. This includes:
- Secure Fencing: Ensure that your yard is securely fenced to prevent your pet from escaping.
- Leash Training: Train your pet to walk on a leash and always keep them leashed when outside.
- Supervision: Supervise your pet when they are outside, especially in unfamiliar areas.
- Identification: Ensure that your pet has proper identification, including a microchip and ID tags.
10.3 PETS.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Pet Safety
At PETS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing pet owners with the information and resources they need to ensure their pet’s safety. We offer:
- Comprehensive Articles: Detailed articles on pet safety, health, and behavior.
- Expert Advice: Expert advice from veterinarians, trainers, and other pet professionals.
- Product Reviews: Honest and unbiased reviews of pet products, including microchips and GPS trackers.
- Community Forum: A community forum where you can connect with other pet owners and share your experiences.
10.4 Call to Action
Take proactive steps to protect your pet today. Visit PETS.EDU.VN to learn more about microchips, GPS trackers, and other pet safety measures. Ensure your pet is microchipped, registered, and properly identified. Consider using a GPS tracker for added peace of mind. Together, we can create a safer world for our beloved pets.
Contact Us:
- Address: 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-987-6543
- Website: pets.edu.vn
FAQ About Pet Microchips and GPS
1. What is a pet microchip?
A pet microchip is a small, electronic device, about the size of a grain of rice, that is implanted under your pet’s skin to provide permanent identification.
2. Do pet microchips have GPS?
No, pet microchips do not have GPS capabilities. They use Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, which only provides identification information when scanned.
3. How does a pet microchip work?
When a scanner is passed over the microchip, it transmits a unique identification number to the scanner. This number is then used to look up your contact information in a microchip registry.
4. Why should I microchip my pet?
Microchipping provides a permanent form of identification that cannot be lost or removed. It significantly increases the chances of reuniting with your pet if they get lost.
5. Is microchipping painful for my pet?
Microchipping is a quick and relatively painless procedure. Most pets experience only minimal discomfort, similar to a routine vaccination.
6. How do I register my pet’s microchip?
You can register your pet’s microchip by visiting the website of the microchip provider and following the instructions to create an account and enter your contact information.
7. How do I update my microchip information?
You can update your microchip information by logging into your account on the microchip registry website and updating your contact details.
8. What is a GPS pet tracker?
A GPS pet tracker is a device that uses satellite technology to track your pet’s location in real-time.
9. How does a GPS pet tracker work?
A GPS pet tracker communicates with GPS satellites to determine its precise coordinates. It then transmits this location data to your smartphone or computer via cellular networks or radio frequencies.
10. What are the benefits of using a GPS pet tracker?
GPS pet trackers offer real-time tracking, geofencing, activity monitoring, and peace of mind for pet owners. They can help you quickly locate your pet if they get lost.
![A happy dog wearing