Can Pets Get Fleas In Winter? Absolutely, and PETS.EDU.VN is here to ensure your beloved companions stay pest-free with proactive flea control and effective prevention strategies. Learn how to identify signs of flea infestations, explore different treatments, and keep your furry friends happy, healthy, and itch-free all year round by choosing flea preventatives, parasite control, and flea lifecycle management.
1. Understanding the Flea Threat in Winter
While many believe fleas disappear in winter, this isn’t always the case. Fleas are resilient and can survive colder temperatures, especially indoors.
1.1. The Myth of Flea Hibernation
Fleas don’t truly hibernate. Outdoor flea populations might decrease, but they don’t vanish entirely. Flea eggs, larvae, and pupae can remain dormant, ready to become active when temperatures rise. According to a study by the American Veterinary Medical Association, flea eggs can survive for several months in sheltered environments, even during winter.
1.2. Indoor Flea Havens
Heated homes provide a perfect refuge for fleas during winter. Comfortable temperatures and humidity allow them to continue their life cycle uninterrupted. A flea infestation can quickly escalate indoors, making year-round flea control essential. The Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine emphasizes that indoor flea populations can thrive even when outdoor temperatures are freezing.
1.3. The Flea Life Cycle: A Year-Round Concern
Understanding the flea life cycle is crucial for effective prevention. Fleas go through four stages:
-
Eggs: Laid on pets, these easily fall off and infest carpets, furniture, and bedding.
-
Larvae: These feed on organic debris, including flea feces (flea dirt).
-
Pupae: Developing within a protective cocoon, pupae can remain dormant for months.
-
Adults: These emerge from the cocoon and immediately seek a host for blood meals.
Even if adult fleas die off in winter, the other stages can persist indoors, leading to a new infestation when conditions become favorable.
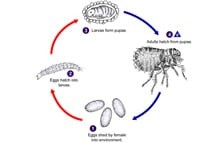 Flea life cycle showcasing eggs, larvae, pupae, and adult fleas
Flea life cycle showcasing eggs, larvae, pupae, and adult fleas
1.4. Why Winter Flea Prevention Matters
Consistent flea prevention protects your pets from discomfort, allergic reactions, and potential diseases transmitted by fleas. Ignoring flea control in winter can lead to a full-blown infestation that’s difficult and costly to eradicate. The Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC) recommends year-round flea prevention for all pets.
2. Identifying Flea Infestations in Winter
Recognizing the signs of a flea infestation early can help you take prompt action.
2.1. Common Symptoms in Pets
-
Excessive Scratching, Biting, or Licking: This is often the first sign that your pet is irritated by fleas.
-
Hair Loss: Constant scratching can lead to hair loss, especially around the tail and hindquarters.
-
Skin Irritation and Redness: Flea bites cause inflammation and can lead to hot spots and secondary infections.
-
Flea Dirt: These are small, black specks in your pet’s fur, which are actually flea feces.
-
Visible Fleas: Adult fleas are small, dark brown insects that move quickly through your pet’s fur.
2.2. Checking Your Pet for Fleas
- Use a Flea Comb: Run a flea comb through your pet’s fur, paying close attention to the base of the tail, groin, and neck.
- Examine the Comb’s Contents: Look for fleas or flea dirt trapped in the comb.
- White Paper Test: Place any debris from the comb on a damp white paper towel. If it turns reddish-brown, it’s likely flea dirt.
- Inspect Bedding and Carpets: Check your pet’s bedding and carpets for signs of fleas or flea dirt.
2.3. Identifying Flea Dirt vs. Regular Dirt
Flea dirt consists of digested blood, so it will dissolve and turn reddish-brown when moistened. Regular dirt will not change color.
| Feature | Flea Dirt | Regular Dirt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Digested blood | Soil, dust, organic matter |
| Color when wet | Reddish-brown | Remains brown or gray |
| Consistency | Dissolves and smears | Retains its shape |
2.4. Recognizing Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD)
Some pets are highly allergic to flea saliva, leading to Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD). Symptoms include intense itching, inflamed skin, hair loss, and secondary skin infections. Even a single flea bite can trigger a severe reaction in sensitive animals. Veterinary dermatologist Dr. Alice Jeromin states that FAD is one of the most common skin conditions in dogs and cats.
3. Winter Flea Prevention Strategies
Protecting your pets and home from fleas requires a multi-pronged approach.
3.1. Year-Round Preventative Medications
- Topical Treatments: Applied to the skin, these medications kill fleas and ticks on contact.
- Oral Medications: Given as a pill or chewable tablet, these work systemically to kill fleas that bite your pet.
- Flea Collars: These release medication that kills fleas and ticks, providing long-lasting protection.
Consult your veterinarian to determine the best preventative medication for your pet’s specific needs and health condition. Medications like selamectin and fipronil are commonly used, but their effectiveness can vary.
3.2. Maintaining a Clean Home Environment
- Regular Vacuuming: Vacuum carpets, rugs, upholstery, and pet bedding frequently to remove flea eggs, larvae, and pupae.
- Wash Bedding Regularly: Wash pet bedding in hot, soapy water at least once a week.
- Steam Cleaning: Steam cleaning carpets and upholstery can kill fleas and their eggs.
- Control Humidity: Use a dehumidifier to reduce humidity levels in your home, making it less hospitable to fleas.
3.3. Yard Maintenance
- Clear Debris: Remove leaves, twigs, and other organic debris from your yard, as these can provide harborage for fleas.
- Mow Regularly: Keep your lawn mowed to reduce shaded areas where fleas thrive.
- Treat Your Yard: Use a flea-control product specifically designed for outdoor use, focusing on shaded areas and pet resting spots.
3.4. Natural Flea Repellents
- Diatomaceous Earth (DE): This natural powder can be sprinkled on carpets and pet bedding to dehydrate and kill fleas. Make sure to use food-grade DE.
- Essential Oils: Some essential oils, such as lavender, cedarwood, and eucalyptus, are known to repel fleas. Dilute the oils with a carrier oil and apply to your pet’s collar or bedding.
- Herbal Flea Sprays: Homemade sprays containing herbs like rosemary, peppermint, and lemon can help repel fleas.
Important Note: Always consult with your veterinarian before using any natural flea repellents, as some can be toxic to pets.
3.5. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM combines multiple strategies to control pests effectively and minimize the use of chemicals. This includes preventative measures, regular monitoring, and targeted treatments.
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Prevention | Maintaining a clean home and yard, using preventative medications | Reduces the likelihood of infestations, minimizes the need for harsh treatments |
| Monitoring | Regularly checking pets and home for signs of fleas | Allows for early detection and intervention |
| Targeted Treatment | Using specific flea control products only when and where needed | Minimizes exposure to chemicals, reduces the risk of resistance |
4. Flea Treatment Options
If your pet already has fleas, several treatment options are available.
4.1. Topical Flea Treatments
- Spot-On Treatments: Applied to a small area of your pet’s skin, these treatments kill adult fleas and prevent re-infestation for up to 30 days. Common ingredients include fipronil, imidacloprid, and selamectin.
- Flea Sprays: These provide immediate relief by killing fleas on contact. Look for sprays containing pyrethrins or permethrin.
- Flea Dips: These involve soaking your pet in a diluted insecticidal solution. Use with caution, as some dips can be toxic. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
4.2. Oral Flea Medications
- Adulticides: These medications kill adult fleas after they bite your pet. Examples include nitenpyram and spinosad.
- Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs): These prevent flea eggs and larvae from developing into adults. Examples include lufenuron and methoprene.
4.3. Flea Shampoos
- Insecticidal Shampoos: These contain ingredients that kill fleas on contact. Use these shampoos as directed, avoiding the eyes and mouth.
- Soothing Shampoos: These can help relieve itching and inflammation caused by flea bites. Look for shampoos containing oatmeal or aloe vera.
4.4. Home Treatments
- Foggers: These release a cloud of insecticide that penetrates hard-to-reach areas. Remove pets, children, and food before using foggers, and follow the instructions carefully.
- Sprays: These can be used to treat carpets, upholstery, and other surfaces where fleas may be hiding.
- Professional Pest Control: For severe infestations, consider hiring a professional pest control company.
4.5. Treating Different Pets
Different pets require different flea treatments. Always consult with your veterinarian before using any flea control product on your pet, especially if they are young, old, pregnant, or have underlying health conditions.
| Pet Type | Recommended Treatments | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Dogs | Topical treatments, oral medications, flea collars, flea shampoos, home treatments | Avoid using products containing permethrin on cats. |
| Cats | Topical treatments specifically formulated for cats, oral medications, flea shampoos, flea combs | Some products safe for dogs are toxic to cats. Always read labels carefully. |
| Rabbits | Flea combs, spot-on treatments specifically formulated for rabbits (with veterinary guidance), careful vacuuming of their environment | Many flea treatments are toxic to rabbits. Consult with a veterinarian experienced in rabbit care before using any product. |
| Small Animals | Regular cage cleaning, flea combs, gentle flea sprays specifically formulated for small animals (with veterinary guidance) | Be cautious with flea control products around small animals like guinea pigs and hamsters, as they are highly sensitive to chemicals. |
5. Addressing Common Flea-Related Issues
Fleas can cause a variety of health problems in pets and humans.
5.1. Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD)
As mentioned earlier, FAD is a common allergic reaction to flea saliva. Treatment involves:
- Strict Flea Control: Eliminating fleas from your pet and their environment is crucial.
- Corticosteroids: These medications can help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: These can help relieve itching in some pets.
- Antibiotics: If a secondary skin infection develops, antibiotics may be necessary.
- Allergy Testing and Immunotherapy: In severe cases, allergy testing and immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be recommended.
5.2. Tapeworms
Fleas can transmit tapeworms to pets. Pets become infected when they ingest fleas carrying tapeworm larvae. Symptoms of tapeworm infection include:
- Visible Tapeworm Segments: These look like small grains of rice around your pet’s anus or in their feces.
- Scooting: Dragging their hindquarters along the ground to relieve itching.
- Weight Loss: In severe cases, tapeworm infection can lead to weight loss.
Treatment involves deworming medication prescribed by your veterinarian.
5.3. Anemia
In severe flea infestations, especially in young or small animals, blood loss can lead to anemia. Symptoms include:
- Pale Gums: Gums that are lighter in color than normal.
- Weakness: Lack of energy and reluctance to move.
- Lethargy: Decreased alertness and responsiveness.
Treatment may involve blood transfusions, iron supplements, and aggressive flea control.
5.4. Preventing Flea Bites on Humans
While fleas prefer animal hosts, they can bite humans, causing itchy red welts. To prevent flea bites:
- Treat Your Pets: Keep your pets on year-round flea prevention.
- Vacuum Regularly: Vacuum carpets, rugs, and upholstery frequently.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When spending time in flea-infested areas, wear long sleeves and pants.
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent containing DEET to your skin.
6. Debunking Flea Myths
There are many misconceptions about fleas. Let’s set the record straight.
6.1. Myth: Fleas Only Live on Pets
Fact: Adult fleas live on pets, but flea eggs, larvae, and pupae can be found throughout your home and yard.
6.2. Myth: Indoor Pets Can’t Get Fleas
Fact: Indoor pets can get fleas from other pets, from humans bringing fleas indoors on their clothing, or from rodents.
6.3. Myth: Fleas Die Off in Winter
Fact: While outdoor flea populations may decrease in winter, fleas can survive indoors and continue to reproduce.
6.4. Myth: Natural Remedies Are Always Safe for Flea Control
Fact: Some natural remedies can be toxic to pets. Always consult with your veterinarian before using any natural flea control product.
6.5. Myth: Once You Get Rid of Fleas, They Won’t Come Back
Fact: Fleas can re-infest your home and pets if you don’t maintain consistent flea prevention.
7. Expert Advice on Flea Control
To provide you with the best information, we’ve consulted with veterinary experts and reviewed the latest research on flea control.
7.1. Consulting with Your Veterinarian
Your veterinarian is your best resource for flea control advice. They can recommend the most effective and safe products for your pet, taking into account their individual needs and health history.
7.2. Staying Updated on New Treatments
The field of flea control is constantly evolving. New products and treatments are always being developed. Stay informed about the latest advances by reading veterinary journals, attending continuing education seminars, and consulting with your veterinarian.
7.3. The Importance of Early Intervention
The sooner you address a flea problem, the easier it will be to control. Don’t wait until your pet is severely infested to take action. Start with preventative measures and monitor your pet regularly for signs of fleas.
7.4. Resources for Pet Owners
-
PETS.EDU.VN: Your go-to source for comprehensive pet care information, including flea control strategies, treatment options, and expert advice.
-
Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC): Provides guidelines for parasite control in pets.
-
American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA): Offers resources for pet owners on a variety of health topics.
8. Creating a Flea-Free Environment
Achieving a flea-free environment requires ongoing effort and a combination of strategies.
8.1. Regular Grooming
Regularly grooming your pet with a flea comb can help remove fleas and flea dirt. This also allows you to monitor your pet for signs of infestation.
8.2. Washing Pet Bedding Frequently
Wash pet bedding in hot, soapy water at least once a week to kill fleas and their eggs.
8.3. Vacuuming Regularly
Vacuum carpets, rugs, upholstery, and floors frequently to remove flea eggs, larvae, and pupae. Pay close attention to areas where your pet spends the most time.
8.4. Treating Your Yard
Treat your yard with a flea control product specifically designed for outdoor use. Focus on shaded areas and pet resting spots.
8.5. Preventing Wildlife Infestations
Wildlife, such as rodents and stray animals, can introduce fleas to your property. Take steps to prevent wildlife infestations by sealing cracks and holes in your home, keeping garbage cans covered, and removing food sources.
9. The Role of PETS.EDU.VN in Flea Prevention
At PETS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing pet owners with the information and resources they need to keep their pets healthy and happy.
9.1. Comprehensive Flea Control Information
Our website features a wealth of articles, guides, and tips on flea control, covering everything from prevention to treatment.
9.2. Product Recommendations
We provide recommendations for safe and effective flea control products, based on expert advice and the latest research.
9.3. Expert Advice from Veterinarians
We partner with veterinarians to provide you with accurate and reliable information on flea control.
9.4. Community Forum
Our community forum allows you to connect with other pet owners, share your experiences, and ask questions about flea control.
9.5. Local Pet Care Services Directory
We maintain a directory of local pet care services, including veterinarians, groomers, and pest control companies, to help you find the resources you need.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Fleas in Winter
Here are some common questions pet owners have about fleas in winter:
- Can my pet get fleas in the winter? Yes, pets can get fleas in the winter, especially if they spend time indoors.
- Do fleas die off in the winter? Outdoor flea populations may decrease, but fleas can survive indoors and continue to reproduce.
- What are the signs of a flea infestation? Excessive scratching, biting, or licking; hair loss; skin irritation; flea dirt; and visible fleas.
- How can I prevent fleas in the winter? Use year-round preventative medications, maintain a clean home environment, and treat your yard.
- What are the best flea treatments for pets? Topical treatments, oral medications, flea shampoos, and flea collars are all effective options.
- How can I treat my home for fleas? Vacuum regularly, wash bedding frequently, and use flea sprays or foggers.
- Are natural flea repellents effective? Some natural repellents can help, but always consult with your veterinarian before using them.
- Can fleas transmit diseases to pets? Yes, fleas can transmit tapeworms and other diseases.
- How can I prevent flea bites on humans? Treat your pets, vacuum regularly, and use insect repellent.
- Where can I get more information about flea control? Visit PETS.EDU.VN or consult with your veterinarian.
Don’t let fleas ruin your pet’s winter. With the right knowledge and strategies, you can keep your furry friends happy, healthy, and itch-free all season long.
Protect your beloved pets from pesky winter fleas! Visit PETS.EDU.VN today for comprehensive information, expert advice, and the best flea control solutions. Our resources will guide you in identifying infestations, choosing effective treatments, and maintaining a flea-free environment for your furry friends. Don’t let fleas compromise your pet’s comfort and health. Trust pets.edu.vn to provide the knowledge and products you need for year-round flea prevention. Contact us at 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-987-6543.