Pet Bottles have become ubiquitous in our daily lives, but what happens to them after we’re done? At PETS.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing insights into responsible pet bottle management, covering everything from recycling advancements to innovative reuse strategies. Discover the power of eco-friendly choices and how you can make a significant impact. Learn about container recovery programs, sustainable plastic, and eco-conscious disposal.
1. Understanding Pet Bottles and Their Impact
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are favored for their clarity, strength, and recyclability. They’re extensively used for beverages, food, and household products. However, their widespread use raises environmental concerns if not properly managed.
1.1. What Are Pet Bottles?
PET, identified by the #1 recycling symbol, is a thermoplastic polymer derived from petroleum. Its properties make it ideal for packaging:
- Durability: Resists impact and wear.
- Lightweight: Reduces transportation costs and environmental impact.
- Clarity: Allows consumers to see the product inside.
- Recyclability: Can be recycled multiple times into new products.
1.2. Environmental Concerns
Despite their recyclability, PET bottles pose environmental threats if they end up in landfills or the natural environment:
- Persistence: PET can take hundreds of years to decompose.
- Pollution: Littered bottles contribute to visual pollution and can harm wildlife.
- Microplastics: Degradation leads to microplastics, which can contaminate soil and water.
- Resource Depletion: Producing new PET bottles requires fossil fuels.
1.3. Economic Impact
The lifecycle of PET bottles affects the economy in several ways:
- Manufacturing: Creates jobs in the plastics industry.
- Recycling: Supports recycling facilities and the creation of new products from recycled PET (rPET).
- Waste Management: Costs associated with collecting, sorting, and disposing of PET bottles.
- Circular Economy: Promotes a circular economy by reducing the need for virgin materials and minimizing waste.
2. Pet Bottle Recycling: Current State and Trends
Recycling PET bottles is crucial for reducing their environmental footprint. The recycling rate and the use of recycled PET are vital indicators of progress.
2.1. Recycling Rates
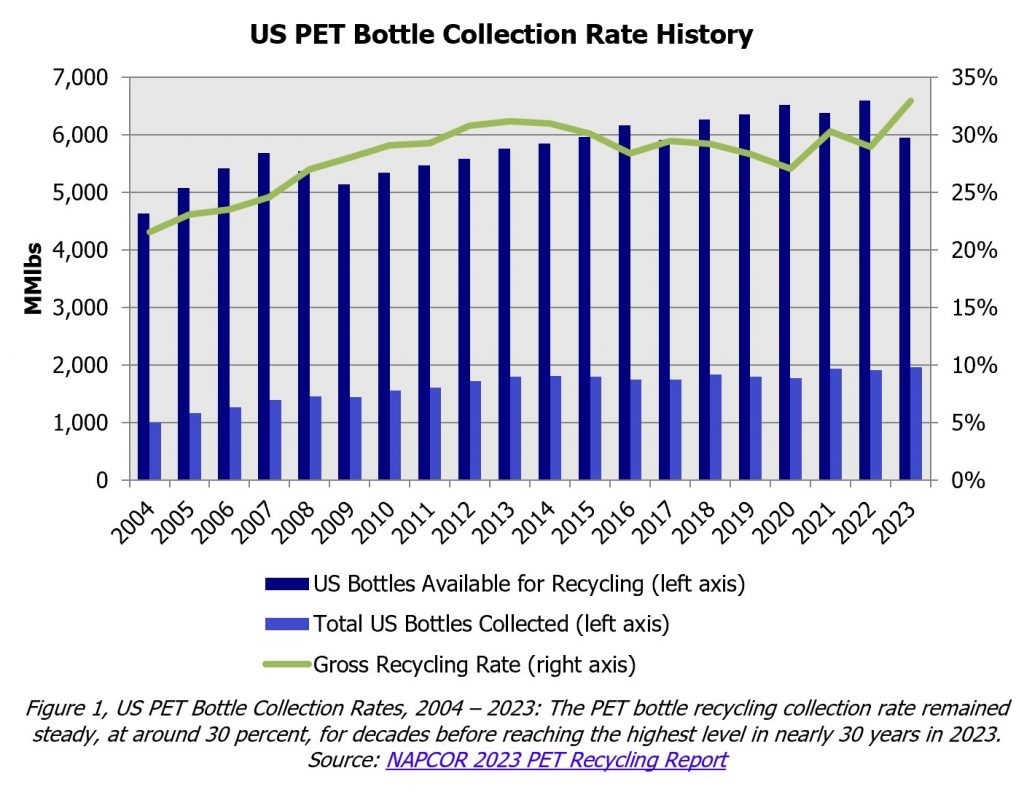
The recycling rate indicates the percentage of PET bottles collected and recycled. Recent data shows improvements in PET bottle recycling rates in the United States.
- United States: In 2023, the PET bottle collection rate reached 33%, up from 29% in 2022, marking the highest rate since 1996, according to the National Association for PET Container Resources (NAPCOR).
- North America: The recycling rate in North America (including the US, Canada, and Mexico) hit a new high of 41.3% in 2023, surpassing the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s global standard.
These figures highlight the increasing focus on recycling and the effectiveness of recycling programs.
2.2. Recycled PET (rPET) Usage
The amount of rPET used in new products, especially bottles and jars, is another critical metric.
- United States: The average amount of rPET used in US bottles and jars reached 16.2% in 2023, up from 13.2% in 2022.
- Increase in Usage: The quantity of rPET used in US bottles in 2023 rose to 966 million pounds, an 11% increase from 870 million pounds in 2022.
The increasing adoption of rPET demonstrates a growing commitment to sustainability among manufacturers and consumers.
2.3. Factors Influencing Recycling Rates
Several factors influence PET bottle recycling rates:
- Collection Programs: Availability of curbside recycling, deposit refund systems, and public drop-off locations.
- Consumer Awareness: Public education campaigns promoting recycling.
- Infrastructure: Efficient sorting and processing facilities.
- Legislation: Mandatory recycled content laws and other regulations.
- Market Demand: Demand for rPET from manufacturers.
Addressing these factors can further improve recycling rates and promote a circular economy.
3. The Recycling Process: From Bottle to New Product
Understanding the recycling process can help consumers appreciate its importance and participate more effectively.
3.1. Collection
PET bottles are collected through various channels:
- Curbside Recycling: Collected from residential homes by municipal or private waste management services.
- Deposit Refund Systems: Consumers receive a refund for returning bottles to designated collection points.
- Drop-Off Centers: Public locations where individuals can drop off recyclables.
- Commercial Recycling: Businesses collect and recycle PET bottles from their operations.
Efficient collection systems are essential for maximizing the amount of PET bottles available for recycling.
3.2. Sorting and Processing
Once collected, PET bottles undergo sorting and processing:
- Sorting: Bottles are sorted by type (PET, HDPE, etc.) and color to ensure quality.
- Cleaning: Bottles are thoroughly washed to remove contaminants.
- Shredding: Bottles are shredded into small flakes.
- Melting: Flakes are melted into molten PET.
- Pelletizing: Molten PET is formed into pellets, which are then used to manufacture new products.
3.3. End Products
Recycled PET can be used to create a variety of products:
- New Bottles: rPET can be used to make new beverage and food containers.
- Textiles: rPET can be spun into fibers for clothing, carpets, and other textiles.
- Packaging: rPET is used in thermoformed packaging for food and consumer goods.
- Strapping: rPET is used to make strapping for bundling and securing products.
- Other Products: rPET can also be used in automotive parts, furniture, and construction materials.
By closing the loop and using rPET to create new products, we reduce the demand for virgin PET and minimize environmental impact.
4. Advantages of Recycling Pet Bottles
Recycling PET bottles offers numerous environmental and economic benefits.
4.1. Environmental Benefits
- Reduced Landfill Waste: Recycling diverts PET bottles from landfills, extending their lifespan and reducing methane emissions.
- Conserved Resources: Recycling reduces the need to extract and process virgin raw materials, such as petroleum.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Manufacturing products from rPET requires less energy than from virgin PET.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Lower energy consumption translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduced Pollution: Recycling reduces pollution associated with the extraction, processing, and transportation of raw materials.
4.2. Economic Benefits
- Job Creation: The recycling industry creates jobs in collection, sorting, processing, and manufacturing.
- Cost Savings: Using rPET can reduce manufacturing costs compared to virgin PET.
- Revenue Generation: Selling rPET generates revenue for recycling facilities and communities.
- Reduced Waste Management Costs: Recycling reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills, lowering disposal costs.
- Circular Economy: Recycling promotes a circular economy, creating a more sustainable and resilient economy.
5. Challenges in Pet Bottle Recycling
Despite the benefits, several challenges hinder PET bottle recycling efforts.
5.1. Contamination
Contamination of PET bottles with other materials (labels, caps, food residue) can reduce the quality of rPET and make it unsuitable for certain applications.
5.2. Collection and Infrastructure
Inadequate collection systems and infrastructure can limit the amount of PET bottles available for recycling.
5.3. Economic Viability
Fluctuations in the price of virgin PET can affect the economic viability of recycling. When virgin PET is cheap, demand for rPET may decrease.
5.4. Public Awareness and Participation
Lack of public awareness and participation can result in low recycling rates. Many consumers are unaware of the importance of recycling or how to properly recycle PET bottles.
5.5. Technological Limitations
Current recycling technologies may not be able to handle certain types of PET bottles or remove all contaminants.
6. Innovations in Pet Bottle Recycling
To overcome these challenges, innovations in PET bottle recycling are crucial.
6.1. Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling, also known as advanced recycling, breaks down PET polymers into their basic building blocks, which can then be used to create virgin-quality PET. This process can handle contaminated or mixed plastic waste that mechanical recycling cannot.
6.2. Enhanced Collection Systems
Implementing more efficient collection systems, such as deposit refund schemes and improved curbside recycling, can increase the amount of PET bottles collected.
6.3. Improved Sorting Technologies
Advanced sorting technologies, such as optical sorting and AI-driven systems, can more accurately separate PET bottles from other materials, reducing contamination.
6.4. Additive Technologies
Additive technologies can improve the properties of rPET, making it suitable for a wider range of applications.
6.5. Biodegradable PET
Research is underway to develop biodegradable PET alternatives that can decompose naturally, reducing the environmental impact of plastic waste.
7. Legislation and Policies Supporting Pet Bottle Recycling
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in promoting PET bottle recycling.
7.1. Mandatory Recycled Content Laws
These laws require manufacturers to include a certain percentage of rPET in their products. This increases demand for rPET and supports the recycling industry.
7.2. Deposit Refund Schemes
Deposit refund schemes incentivize consumers to return PET bottles for recycling by offering a monetary refund.
7.3. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
EPR policies hold producers responsible for the end-of-life management of their products, including PET bottles.
7.4. Landfill Bans
Banning PET bottles from landfills can encourage recycling and reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills.
7.5. Public Awareness Campaigns
Government-sponsored public awareness campaigns can educate consumers about the importance of recycling and how to properly recycle PET bottles.
8. Consumer Tips for Effective Pet Bottle Recycling
Consumers play a vital role in ensuring the success of PET bottle recycling efforts.
8.1. Rinse and Empty Bottles
Rinsing and emptying PET bottles before recycling removes food residue and other contaminants that can reduce the quality of rPET.
8.2. Remove Caps and Labels
While some recycling facilities can handle caps and labels, removing them can improve the efficiency of the recycling process.
8.3. Flatten Bottles
Flattening PET bottles can save space in recycling bins and make them easier to transport.
8.4. Recycle Properly
Make sure to recycle PET bottles in designated recycling bins and follow local recycling guidelines.
8.5. Buy Products Made from rPET
Supporting products made from rPET increases demand for recycled materials and encourages manufacturers to use them.
9. The Role of Pets.Edu.Vn in Promoting Pet Bottle Recycling
At PETS.EDU.VN, we are committed to promoting sustainable practices, including PET bottle recycling.
9.1. Education and Awareness
We provide educational resources and articles on the importance of PET bottle recycling, the recycling process, and the benefits of using rPET.
9.2. Community Engagement
We engage with our community to promote recycling initiatives and encourage participation in local recycling programs.
9.3. Partnering with Recycling Organizations
We partner with recycling organizations to support their efforts and promote best practices in PET bottle recycling.
9.4. Advocacy
We advocate for policies and regulations that support PET bottle recycling and promote a circular economy.
9.5. Leading by Example
We strive to minimize our own environmental footprint by using rPET in our packaging and promoting sustainable practices within our organization.
10. Future Trends in Pet Bottle Recycling
The future of PET bottle recycling looks promising, with several emerging trends and technologies poised to transform the industry.
10.1. Increased Use of Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling is expected to play a larger role in PET bottle recycling, allowing for the processing of more complex and contaminated waste streams.
10.2. Advanced Sorting Technologies
Advanced sorting technologies will improve the efficiency and accuracy of PET bottle sorting, reducing contamination and increasing the quality of rPET.
10.3. Bioplastics and Biodegradable Alternatives
The development and adoption of bioplastics and biodegradable alternatives to PET could reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste.
10.4. Closed-Loop Systems
More companies are adopting closed-loop systems, where PET bottles are collected, recycled, and used to make new bottles, creating a truly circular economy.
10.5. Smart Packaging
Smart packaging technologies, such as QR codes and NFC tags, can provide consumers with information about the recyclability of PET bottles and encourage proper disposal.
11. Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Pet Bottle Management
PET bottles are a ubiquitous part of modern life, but their environmental impact can be minimized through effective recycling practices. By understanding the importance of PET bottle recycling, supporting recycling initiatives, and adopting sustainable practices, we can reduce waste, conserve resources, and protect the environment. At PETS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to make a positive impact.
11.1. Call to Action
Join us in promoting sustainable PET bottle management. Visit PETS.EDU.VN for more information on recycling, sustainable packaging, and other eco-friendly practices. Contact us at 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States, or Whatsapp at +1 555-987-6543.
Together, we can create a cleaner, greener future for all. Explore our website to discover more about responsible pet care and environmental stewardship. Your journey towards sustainable pet ownership starts here.
12. Case Studies: Successful Pet Bottle Recycling Programs
Examining successful recycling programs can provide valuable insights and inspire further action.
12.1. Germany’s Deposit Refund System
Germany’s deposit refund system, known as “Pfand,” has been highly successful in achieving high recycling rates for PET bottles. Consumers pay a deposit when purchasing a beverage in a PET bottle and receive a refund when they return the bottle to a designated collection point.
- Key Features:
- Mandatory deposit on PET bottles.
- Widespread network of collection points.
- High consumer participation.
- Results:
- High recycling rates (over 90%).
- Reduced littering.
- Increased availability of high-quality rPET.
12.2. Norway’s Infinitum System
Norway’s Infinitum system is another successful deposit refund scheme that has achieved high recycling rates for PET bottles. The system is managed by a non-profit organization and includes a comprehensive network of collection points and advanced sorting technologies.
- Key Features:
- Mandatory deposit on PET bottles.
- Efficient collection and sorting system.
- Strong collaboration between stakeholders.
- Results:
- High recycling rates (over 95%).
- Reduced environmental impact.
- Increased use of rPET in new products.
12.3. California’s Bottle Bill
California’s Bottle Bill, also known as the California Beverage Container Recycling and Litter Reduction Act, provides a deposit refund for certain beverage containers, including PET bottles. The program has helped to increase recycling rates and reduce litter in the state.
- Key Features:
- Deposit refund on beverage containers.
- Network of recycling centers and collection points.
- Public education campaigns.
- Results:
- Increased recycling rates.
- Reduced litter.
- Support for recycling infrastructure.
13. Pet Bottle Alternatives: Reducing Reliance on Plastic
While recycling is crucial, reducing our reliance on PET bottles altogether is an even more sustainable approach.
13.1. Reusable Water Bottles
Using reusable water bottles made from stainless steel, glass, or BPA-free plastic can significantly reduce the number of PET bottles consumed.
13.2. Water Filters
Installing a water filter at home can eliminate the need to purchase bottled water altogether.
13.3. Refill Stations
Supporting businesses that offer refill stations for water, soap, and other products can reduce the demand for PET bottles.
13.4. Concentrated Products
Buying concentrated products, such as cleaning solutions and detergents, can reduce the amount of packaging required.
13.5. Package-Free Stores
Shopping at package-free stores can eliminate the need for PET bottles and other single-use packaging.
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Pet Bottle Recycling
14.1. What are PET bottles made of?
PET bottles are made of polyethylene terephthalate, a type of plastic resin.
14.2. Can PET bottles be recycled?
Yes, PET bottles are highly recyclable and can be recycled into new bottles, textiles, and other products.
14.3. How many times can a PET bottle be recycled?
PET bottles can be recycled multiple times, although the quality of the rPET may decrease with each cycle.
14.4. What is rPET?
rPET stands for recycled polyethylene terephthalate, which is PET that has been recycled from post-consumer waste.
14.5. Why is it important to recycle PET bottles?
Recycling PET bottles reduces landfill waste, conserves resources, lowers energy consumption, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
14.6. How can I recycle PET bottles properly?
Rinse and empty the bottles, remove caps and labels, flatten the bottles, and recycle them in designated recycling bins.
14.7. What are the challenges in PET bottle recycling?
Challenges include contamination, inadequate collection and infrastructure, economic viability, and lack of public awareness.
14.8. What are some innovations in PET bottle recycling?
Innovations include chemical recycling, enhanced collection systems, improved sorting technologies, and biodegradable PET alternatives.
14.9. What is the role of government in promoting PET bottle recycling?
Governments can implement mandatory recycled content laws, deposit refund schemes, extended producer responsibility policies, and public awareness campaigns.
14.10. How can PETS.EDU.VN help me learn more about PET bottle recycling?
pets.edu.vn provides educational resources, community engagement, partnerships with recycling organizations, and advocacy for sustainable practices.
15. Advanced Recycling Technologies for Pet Bottles
Beyond traditional mechanical recycling, advanced technologies are emerging to handle more complex plastic waste.
15.1. Depolymerization
This process breaks down PET polymers into their original monomers, which can then be used to create virgin-quality PET.
- Benefits:
- Handles contaminated or mixed plastic waste.
- Produces virgin-quality PET.
- Reduces the need for fossil fuels.
- Challenges:
- High energy consumption.
- Complex technology.
- High capital investment.
15.2. Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis involves heating plastic waste in the absence of oxygen to produce oil, gas, and char. The oil can then be refined into new plastics or fuels.
- Benefits:
- Handles a wide range of plastic waste.
- Produces valuable byproducts.
- Reduces landfill waste.
- Challenges:
- Air pollution.
- Complex technology.
- Variable product quality.
15.3. Gasification
Gasification converts plastic waste into syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be used to produce chemicals, fuels, or electricity.
- Benefits:
- Handles a wide range of plastic waste.
- Produces versatile syngas.
- Reduces landfill waste.
- Challenges:
- High capital investment.
- Complex technology.
- Air pollution.
16. The Impact of Microplastics from Pet Bottles
The degradation of PET bottles in the environment can lead to the formation of microplastics, which pose a threat to ecosystems and human health.
16.1. What are Microplastics?
Microplastics are small plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size. They can come from the breakdown of larger plastic items, such as PET bottles, or from microplastic beads used in personal care products.
16.2. Sources of Microplastics
- Plastic Litter: The breakdown of plastic litter in the environment.
- Wastewater Treatment Plants: Microplastics that pass through wastewater treatment plants.
- Industrial Processes: Microplastics released from industrial processes.
- Personal Care Products: Microplastic beads used in scrubs and toothpaste.
16.3. Environmental Impact
- Water Pollution: Microplastics contaminate rivers, lakes, and oceans, harming aquatic life.
- Soil Contamination: Microplastics accumulate in soil, affecting plant growth and soil health.
- Wildlife Harm: Animals ingest microplastics, leading to starvation, poisoning, and other health problems.
16.4. Human Health Impact
- Ingestion: Humans ingest microplastics through contaminated food and water.
- Inhalation: Microplastics can be inhaled from the air.
- Toxicity: Microplastics can release toxic chemicals into the body.
16.5. Solutions
- Reduce Plastic Consumption: Reduce the use of single-use plastics, including PET bottles.
- Proper Waste Management: Dispose of plastic waste properly to prevent it from entering the environment.
- Advanced Recycling Technologies: Use advanced recycling technologies to break down plastic waste into its basic building blocks.
- Microplastic Filters: Install microplastic filters in wastewater treatment plants and washing machines.
17. The Role of Consumers in Promoting Circular Economy for Pet Bottles
Consumers have a crucial role in promoting a circular economy for PET bottles through their purchasing decisions, recycling habits, and advocacy efforts.
17.1. Purchasing Decisions
- Choose Products with Minimal Packaging: Opt for products with minimal packaging to reduce the amount of plastic waste generated.
- Buy Products Made from rPET: Support products made from recycled PET to increase demand for recycled materials.
- Avoid Single-Use Plastics: Choose reusable alternatives to single-use plastics, such as water bottles, shopping bags, and food containers.
17.2. Recycling Habits
- Recycle Properly: Follow local recycling guidelines and ensure that PET bottles are properly cleaned and sorted before recycling.
- Participate in Deposit Refund Programs: Take advantage of deposit refund programs to incentivize recycling and reduce litter.
- Support Local Recycling Initiatives: Support local recycling initiatives and advocate for improved recycling infrastructure.
17.3. Advocacy Efforts
- Educate Others: Share information about the importance of PET bottle recycling and the benefits of a circular economy.
- Support Legislation: Advocate for policies that promote recycling and reduce plastic waste.
- Contact Manufacturers: Contact manufacturers and encourage them to use more recycled materials in their products.
- Join Environmental Organizations: Join environmental organizations and participate in advocacy campaigns.
18. Emerging Trends in Sustainable Packaging for Pet Bottles
The packaging industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and technologies emerging to make PET bottles more sustainable.
18.1. Bio-Based PET
Bio-based PET is made from renewable resources, such as sugarcane or corn, rather than fossil fuels.
- Benefits:
- Reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Lower carbon footprint.
- Renewable resource.
- Challenges:
- Higher cost.
- Limited availability.
- Potential land use impacts.
18.2. Compostable PET Alternatives
Compostable PET alternatives are designed to break down in compost facilities, reducing the amount of plastic waste sent to landfills.
- Benefits:
- Reduces landfill waste.
- Breaks down in compost facilities.
- Environmentally friendly.
- Challenges:
- Requires specific composting conditions.
- Limited availability.
- Potential for contamination of recycling streams.
18.3. Lightweighting
Lightweighting involves reducing the amount of material used to produce PET bottles, without compromising their performance.
- Benefits:
- Reduces resource consumption.
- Lower transportation costs.
- Reduced carbon footprint.
- Challenges:
- Requires advanced technology.
- Potential for reduced durability.
18.4. Recycled Content Certification
Recycled content certification provides assurance that products contain a certain percentage of recycled materials.
- Benefits:
- Increases transparency.
- Builds consumer trust.
- Supports the recycling industry.
- Challenges:
- Requires independent verification.
- Can be costly.
19. Collaborations and Partnerships for Enhancing Pet Bottle Recycling
Collaborations and partnerships between governments, businesses, and organizations are essential for enhancing PET bottle recycling efforts.
19.1. Government Initiatives
Governments can implement policies and regulations that promote recycling, such as mandatory recycled content laws, deposit refund schemes, and extended producer responsibility policies.
19.2. Business Initiatives
Businesses can invest in recycling infrastructure, use more recycled materials in their products, and develop sustainable packaging solutions.
19.3. Organization Partnerships
Organizations can provide educational resources, advocate for policy changes, and support recycling initiatives.
19.4. Community Engagement
Engaging with communities to promote recycling and reduce plastic waste is essential for creating a sustainable future.
20. The Future of Pet Bottle Waste Management: A Sustainable Vision
The future of PET bottle waste management should focus on creating a sustainable vision that prioritizes waste reduction, recycling, and circular economy principles.
20.1. Waste Reduction
Reducing the amount of PET bottle waste generated is the first step towards sustainability. This can be achieved through the use of reusable alternatives, minimal packaging, and concentrated products.
20.2. Recycling
Recycling PET bottles properly is crucial for conserving resources, reducing landfill waste, and minimizing environmental impact. This can be achieved through improved collection systems, advanced sorting technologies, and increased public awareness.
20.3. Circular Economy
Adopting circular economy principles is essential for creating a sustainable future for PET bottle waste management. This involves designing products for recyclability, using more recycled materials, and creating closed-loop systems where PET bottles are collected, recycled, and used to make new bottles.
20.4. Innovation
Investing in research and development of innovative technologies, such as chemical recycling, bio-based PET, and compostable alternatives, is crucial for transforming the PET bottle waste management industry.
20.5. Collaboration
Collaboration between governments, businesses, organizations, and communities is essential for achieving a sustainable vision for PET bottle waste management. By working together, we can create a cleaner, greener future for all.