Can You Track A Chipped Pet? Absolutely! At PETS.EDU.VN, we understand the heartache of a lost pet, and we’re here to clarify how microchipping can help reunite you with your furry friend. Microchips greatly improve the chances of a safe return by providing a permanent form of identification. Explore effective pet recovery strategies, understand microchip registration, and discover the role of RFID technology with PETS.EDU.VN.
1. Understanding Microchips: Your Pet’s Permanent ID
Microchips are small, electronic devices, about the size of a grain of rice, implanted under your pet’s skin. These chips use Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, providing a unique identification number that can be scanned by veterinarians, animal shelters, and pet professionals. Unlike GPS trackers, microchips don’t track your pet’s location in real-time. Instead, they store vital information that helps identify your pet and contact you if they’re found.
1.1 How Microchips Work
When a microchip scanner is passed over the area where the chip is implanted, the chip emits a radio signal containing its unique ID number. This number is then used to access a database containing your contact information.
1.2 Key Benefits of Microchipping
- Permanent Identification: Microchips cannot be easily removed or altered, providing a reliable form of identification for your pet.
- Increased Recovery Rate: Studies show that microchipped pets are significantly more likely to be reunited with their owners.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your pet has a microchip can provide peace of mind, especially if they have a tendency to wander.
2. Microchips vs. GPS Trackers: Knowing the Difference
It’s essential to distinguish between microchips and GPS trackers. While both can help you recover a lost pet, they function very differently. Microchips are passive devices that store information, while GPS trackers actively transmit location data.
| Feature | Microchip | GPS Tracker |
|---|---|---|
| Tracking Ability | No real-time tracking | Real-time tracking |
| Power Source | No battery required | Requires battery and charging |
| Data Transmittal | Only transmits data when scanned | Continuously transmits location data |
| Size | Small, grain-of-rice size | Larger, collar-mounted device |
| Cost | One-time cost for implantation and registration | Ongoing costs for device and subscription |

2.1 GPS Trackers: Real-Time Location Monitoring
GPS trackers use satellite technology to pinpoint your pet’s location, allowing you to monitor their movements through a smartphone app or web interface.
2.2 Microchips: Identification and Reunification
Microchips serve as a permanent ID, ensuring your pet can be identified and returned to you if they end up at a shelter or veterinary clinic.
3. The Importance of Microchip Registration
A microchip is only as good as the information linked to it. Registering your pet’s microchip with your current contact details is crucial for successful reunification. Without accurate registration, the microchip is essentially useless.
3.1 How to Register Your Pet’s Microchip
- Locate the Microchip Number: Your veterinarian or the shelter where you adopted your pet can provide you with the microchip number.
- Choose a Registry: Several national and international microchip registries exist. Select a reputable registry.
- Create an Account: Most registries allow you to create an online account to manage your pet’s information.
- Enter Your Pet’s Information: Provide your pet’s name, breed, age, and any other relevant details.
- Enter Your Contact Information: Include your name, address, phone number, and email address.
- Keep Your Information Updated: Whenever you move or change your phone number, update your pet’s microchip registration immediately.
3.2 Verifying Your Microchip Registration
Use the American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) Microchip Lookup Tool (https://www.aaha.org/petmicrochiplookup) to verify that your pet’s microchip is registered and that your contact information is correct.
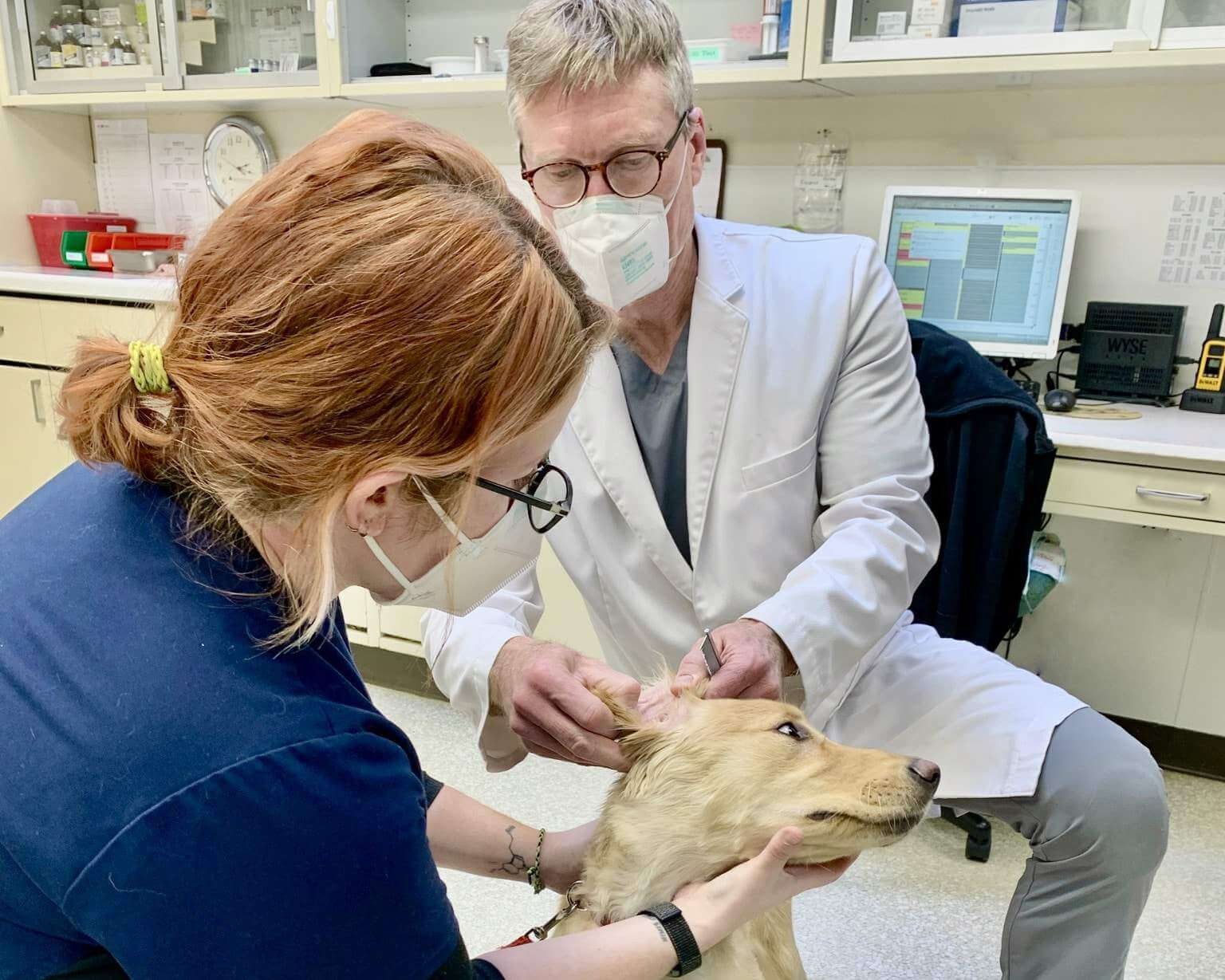
4. Understanding Microchip Scanning Procedures
When a lost pet is found and taken to a veterinary clinic or animal shelter, one of the first things they do is scan for a microchip. This process is quick, painless, and essential for identifying the pet and contacting the owner.
4.1 Who Can Scan a Microchip?
- Veterinarians
- Animal Shelters
- Animal Control Officers
- Some Pet Stores and Rescue Organizations
4.2 The Scanning Process
- The scanner is passed over the area between the pet’s shoulder blades.
- If a microchip is present, the scanner will display the unique ID number.
- The ID number is then used to search the microchip registry for the owner’s contact information.
- The owner is contacted, and arrangements are made to reunite them with their pet.
5. Taking Action When Your Chipped Pet Goes Missing
Even with a microchip, it’s important to take proactive steps to find your lost pet. Here are some immediate actions you should take:
5.1 Steps to Take Immediately
- Search Your Neighborhood: Walk or drive around your neighborhood, calling your pet’s name.
- Contact Local Shelters and Animal Control: Notify them that your pet is missing and provide a description and your contact information.
- Post Flyers: Create flyers with a photo of your pet and your contact information, and post them in your neighborhood and local businesses.
- Use Social Media: Share photos and information about your lost pet on social media platforms, and ask your friends and neighbors to share as well.
- Check Online Lost and Found Pet Sites: Many websites and online forums are dedicated to helping reunite lost pets with their owners.
5.2 Utilizing the Microchip Registry
- Update Your Pet’s Status: Log in to your microchip registry account and mark your pet as lost. This will alert the registry if anyone scans your pet’s microchip.
- Verify Your Contact Information: Ensure that your contact information is current and accurate.
6. Microchip Technology: A Closer Look
Understanding the technology behind microchips can help you appreciate their importance and limitations.
6.1 RFID Technology
Microchips use RFID technology, which relies on radio waves to transmit information. The microchip itself is passive, meaning it doesn’t have its own power source. It only becomes active when scanned by a microchip reader.
6.2 ISO Compliance
Many microchips are ISO compliant, meaning they meet international standards for microchip technology. This ensures that the microchip can be read by any ISO-compliant scanner, regardless of the manufacturer.
6.3 Microchip Migration
In rare cases, a microchip can migrate from its original implantation site. However, most microchips are coated with a biocompatible material that helps prevent migration.
7. Choosing the Right Microchip for Your Pet
With various microchip options available, it’s important to choose the right one for your pet. Consider the following factors:
7.1 Factors to Consider
- ISO Compliance: Ensure the microchip is ISO compliant for universal readability.
- Registry Options: Research the microchip registry associated with the microchip and ensure it’s reputable and reliable.
- Additional Features: Some microchips offer additional features, such as online pet profiles or emergency medical alerts.
7.2 Save This Life™ Microchips
Save This Life™ microchips are a popular choice, offering innovative features such as a metal collar tag with a unique identification number. When someone finds your pet and enters the number into Google, you’ll receive text and email notifications with contact information and location.
8. Addressing Common Concerns About Microchips
Many pet owners have questions and concerns about microchips. Let’s address some of the most common ones:
8.1 Can a Microchip Cause Cancer?
Studies have shown that the risk of microchip-related cancer is extremely low. The benefits of microchipping far outweigh the potential risks.
8.2 Can a Microchip Be Removed?
While it’s possible to remove a microchip, it’s generally not recommended unless there’s a medical reason. The removal process requires a surgical procedure and may not be worth the risk.
8.3 Can a Microchip Fail?
Microchip failure is rare, but it can happen. It’s important to have your veterinarian scan your pet’s microchip periodically to ensure it’s still functioning properly.
9. Legal and Ethical Considerations of Microchipping
Microchipping has become an integral part of responsible pet ownership. Many local governments and organizations have established guidelines and regulations surrounding microchipping to promote pet safety and accountability. Let’s delve deeper into the legal and ethical dimensions of microchipping.
9.1 Legal Requirements for Microchipping
In several regions, microchipping is mandated by law for specific types of pets, particularly dogs. These laws aim to facilitate the swift return of lost pets to their families and ensure responsible pet ownership. Compliance with these regulations might involve monetary penalties or legal ramifications for non-compliance.
9.2 Ethical Obligations for Pet Owners
Beyond the legal requirements, there exists an ethical obligation for pet owners to microchip their pets. Microchipping demonstrates a commitment to the safety and well-being of the pet, increasing the likelihood of reunification in case of loss. It also aids in holding owners responsible for their pet’s behavior and welfare, fostering responsible pet ownership.
9.3 Data Privacy and Security
When entrusting a pet’s information to a microchip registry, it’s crucial to contemplate data privacy and security. Opt for reliable registries that adhere to stringent data protection protocols to ensure the confidentiality of personal information. Comprehend the registry’s privacy policies and data management practices to make well-informed decisions.
10. New Trends and Innovations in Microchip Technology
As technology progresses, so does the realm of pet microchips. Emerging trends and innovations are enhancing the functionality and effectiveness of microchips, providing pet owners with even more resources to safeguard their cherished companions. Let’s explore some of the latest advancements in microchip technology.
10.1 GPS-Enabled Microchips
While conventional microchips lack GPS tracking capabilities, researchers are exploring the development of GPS-enabled microchips that can supply real-time location data for lost pets. These innovative microchips could revolutionize pet recovery attempts, enabling owners to precisely pinpoint their pet’s whereabouts.
10.2 Temperature-Sensing Microchips
Innovative microchips are being engineered to include temperature sensors that can monitor a pet’s body temperature internally. This feature can be particularly beneficial for detecting early signs of illness or infection, empowering pet owners to seek timely veterinary care.
10.3 Integration with Smart Home Devices
Envision a future where your pet’s microchip seamlessly integrates with your smart home devices. This integration could enable features such as automated pet feeding, remote health monitoring, and tailored environmental controls based on your pet’s specific requirements.
11. Understanding Different Types of Microchips
Not all microchips are created equal. There are various types available, each with its own set of features and benefits. Knowing the distinctions between these microchips can help you make an informed decision when selecting one for your beloved pet.
11.1 Standard Microchips
These are the most prevalent type of microchips used in pets. They operate on radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology, assigning a distinct identification number that can be scanned by veterinarians and animal shelters.
11.2 Encrypted Microchips
Employing advanced encryption technology, these microchips offer enhanced security and deter fraudulent activities. They are perfect for pets with heightened security requirements, such as service animals or competitive animals.
11.3 Programmable Microchips
These adaptable microchips enable pet owners to store extra data, such as medical records, allergies, and emergency contact details. This data can be readily accessed by scanning the microchip, providing vital details in crucial circumstances.
12. Maintaining Your Pet’s Microchip
Ensuring that your pet’s microchip remains functional and up to date is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness. Regular maintenance and care can help prevent complications and guarantee that your pet can be identified and reunited with you if they ever get lost.
12.1 Regular Check-Ups
During your pet’s routine veterinary check-ups, ask your veterinarian to scan the microchip to confirm that it is still functioning correctly. This simple procedure can help detect any potential issues early on.
12.2 Proper Storage
Store your pet’s microchip registration information in a secure location where you can easily access it when needed. This includes the microchip number, registry contact information, and your pet’s profile details.
12.3 Timely Reporting
In the unfortunate event that your pet goes missing, promptly report it to the microchip registry and local animal shelters. Provide them with your pet’s microchip number and any other relevant information to aid in the search efforts.
13. Debunking Common Myths About Microchips
Despite their widespread use, several myths and misconceptions surround pet microchips. Let’s debunk some of these common myths and shed light on the truth about microchips.
13.1 Myth: Microchips Can Track Your Pet’s Location
Fact: As discussed earlier, microchips do not have GPS tracking capabilities. They rely on RFID technology, which only transmits information when scanned by a compatible device.
13.2 Myth: Microchips Are a Substitute for Collars and ID Tags
Fact: While microchips provide permanent identification, they should not replace collars and ID tags. Collars and tags offer immediate identification for your pet and can help prevent them from ending up in a shelter in the first place.
13.3 Myth: Microchips Are Expensive
Fact: The cost of microchipping is relatively affordable, especially when considering the peace of mind and increased chances of reuniting with your pet. Many veterinary clinics and animal shelters offer microchipping services at reasonable rates.
14. Microchipping Exotic Pets: Special Considerations
While microchipping is commonly associated with dogs and cats, it can also be beneficial for exotic pets such as birds, reptiles, and small mammals. However, there are special considerations to keep in mind when microchipping exotic pets.
14.1 Species-Specific Guidelines
Different species have different anatomical considerations that can affect the placement and effectiveness of microchips. Consult with a veterinarian experienced in exotic pet care to determine the appropriate microchipping technique for your pet.
14.2 Anesthesia Requirements
Some exotic pets may require anesthesia or sedation during the microchipping procedure to minimize stress and ensure accurate placement of the microchip. Your veterinarian can advise you on whether anesthesia is necessary for your pet.
14.3 Registration Challenges
Not all microchip registries accept registrations for exotic pets. Research and identify registries that specifically cater to exotic animals to ensure that your pet’s microchip is properly registered and traceable.
15. The Role of Microchips in Disaster Preparedness
In times of natural disasters or emergencies, microchips can play a vital role in reuniting displaced pets with their families. Disaster preparedness plans should include microchipping as a key component to ensure the safety and well-being of pets during and after a crisis.
15.1 Pre-Disaster Planning
Before a disaster strikes, ensure that your pet is microchipped and that your contact information is up to date in the microchip registry. Create a disaster preparedness kit for your pet that includes essential supplies such as food, water, medication, and identification documents.
15.2 Post-Disaster Recovery
Following a disaster, promptly search for your pet and report them missing to local animal shelters and rescue organizations. Check online lost and found pet websites and social media groups for any leads or sightings of your pet.
15.3 Collaboration with Relief Efforts
Work closely with disaster relief organizations and animal rescue teams to facilitate the search and recovery efforts for lost pets. Provide them with your pet’s microchip number and any other relevant information to aid in the reunification process.
At PETS.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with the most up-to-date and reliable information on pet care. We understand the unique challenges pet owners face, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
For more in-depth knowledge and resources, be sure to visit PETS.EDU.VN. Our website offers a wealth of information on various pet topics, including:
- Detailed guides on pet health and nutrition
- Tips for training and behavior modification
- Reviews of pet products and services
- A community forum where you can connect with other pet owners
Contact Us:
- Address: 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-987-6543
- Website: PETS.EDU.VN
We at pets.edu.vn wish you the best of luck as you set off on this exciting adventure!
FAQ: Microchips and Pet Tracking
Here are some frequently asked questions about microchips and pet tracking:
- Can a microchip track my pet’s location in real-time? No, microchips do not have GPS capabilities and cannot track your pet’s location in real-time.
- How do microchips help find lost pets? Microchips provide a permanent form of identification that can be scanned by veterinarians and shelters to identify your pet and contact you.
- Is it necessary to register my pet’s microchip? Yes, registering your pet’s microchip with your current contact information is crucial for successful reunification.
- What information is stored on a microchip? Microchips store a unique identification number that is linked to your contact information in a microchip registry.
- Can I update my contact information on the microchip registry? Yes, you can update your contact information on the microchip registry online or by contacting the registry directly.
- Are microchips safe for pets? Yes, microchips are generally safe for pets. The risk of microchip-related complications is very low.
- Can any vet scan a microchip? Yes, most veterinarians have microchip scanners and can scan your pet for a microchip.
- Can a microchip be removed from a pet? While it’s possible to remove a microchip, it’s generally not recommended unless there’s a medical reason.
- How much does it cost to microchip a pet? The cost of microchipping varies depending on your location and veterinarian, but it typically ranges from $25 to $75.
- What should I do if I find a lost pet with a microchip? Take the pet to a veterinarian or animal shelter to have the microchip scanned and contact the owner.