Are you curious if Can You Keep A Desert Rain Frog As A Pet? At PETS.EDU.VN, we provide an in-depth guide about desert rain frogs, their unique characteristics, and whether they make suitable pets, offering practical advice and addressing concerns. This article will cover everything from setting up their habitat to understanding their dietary needs, ensuring you’re well-prepared to care for these amazing amphibians, enhancing your knowledge of amphibian care and responsible pet ownership. Keep reading to discover everything you need to know about desert rain frog care, desert frog environment, and pet amphibian ownership.
1. Desert Rain Frog: An Overview
| Common Name: | Desert Rain Frog |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name: | Breviceps macrops |
| Other Names: | Boulenger’s short-headed frog, Web-footed rain frog |
| Group Name: | Army, Colony |
| Adult Length: | 1.5-2.5 inches (4-6 cm) |
| Adult Weight: | 0.39-0.49 ounces (11-14 grams) |
| Color: | Yellowish-Brown |
| Skin Type: | Transparent |
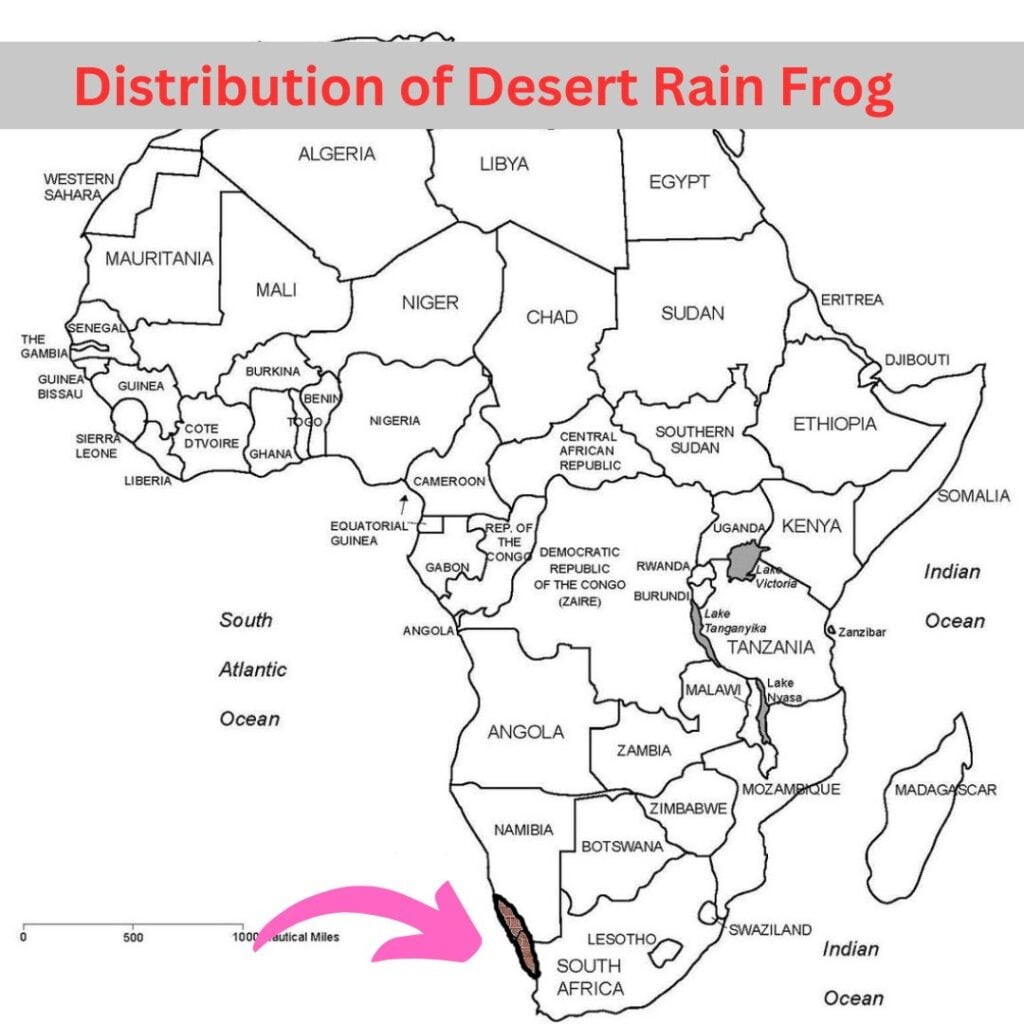
| Distribution: | Namibia, South Africa |
| Habitat: | Sand dunes |
| Characteristics: | Nocturnal |
| Lives in: | Burrows in moist soil, 4-8 inches (10-20 cm) deep |
| Vocal Sound: | High-pitched squeak during mating season |
| Breeding Season: | June-October |
| Litter Size: | 12-40 |
| Distinctive Feature: | Transparent skin, high-pitch squeak, direct development from eggs, stout body with small legs |
| Diets: | Moths, beetles, insect larvae |
| Predators: | Eagles, Honey Badgers, Snakes, Antelopes |
| Life Span: | 3-5 years (up to 15 years in captivity) |
| Speed: | Up to 6 mph (10 km/h) |
| Threats: | Diamond mining, road construction, human settlement, hunting |
| IUCN Status: | Near Threatened |
| Can be a pet? | Yes |





1.1. Detailed Scientific Classification
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
|---|---|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Brevicipitidae |
| Genus: | Breviceps |
| Species: | Breviceps macrops |
2. Unveiling 10 Amazing Facts About Desert Rain Frogs
2.1. Physical Traits of the Desert Rain Frog
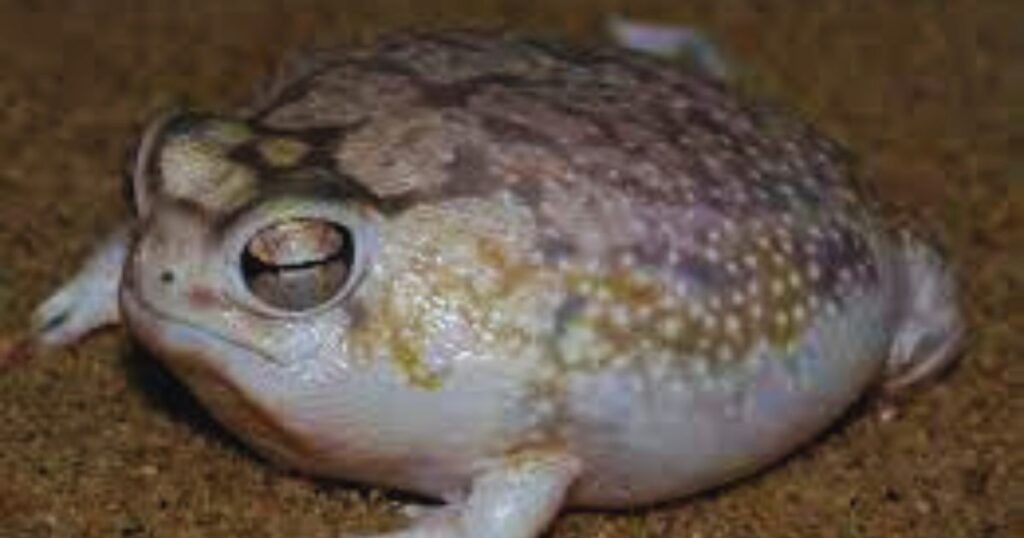
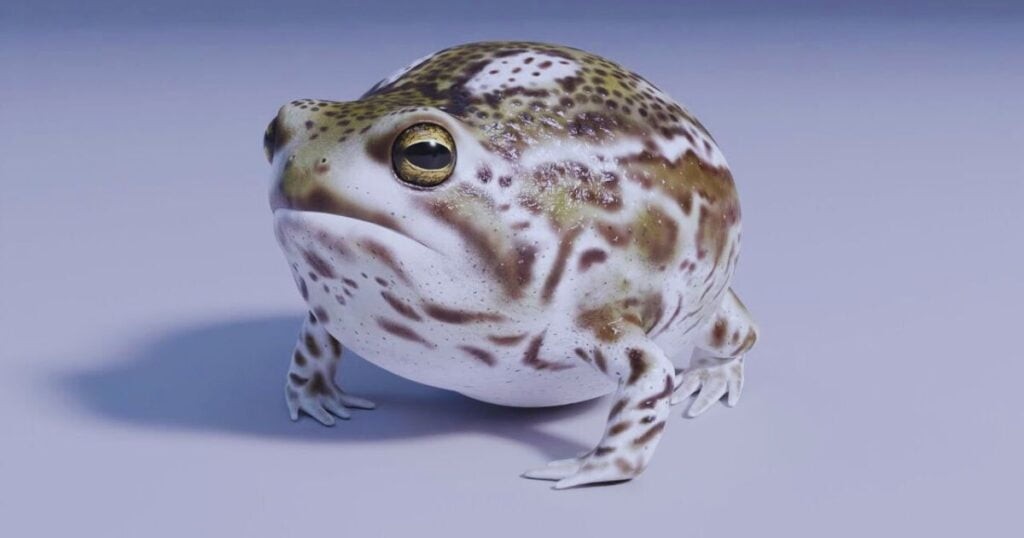
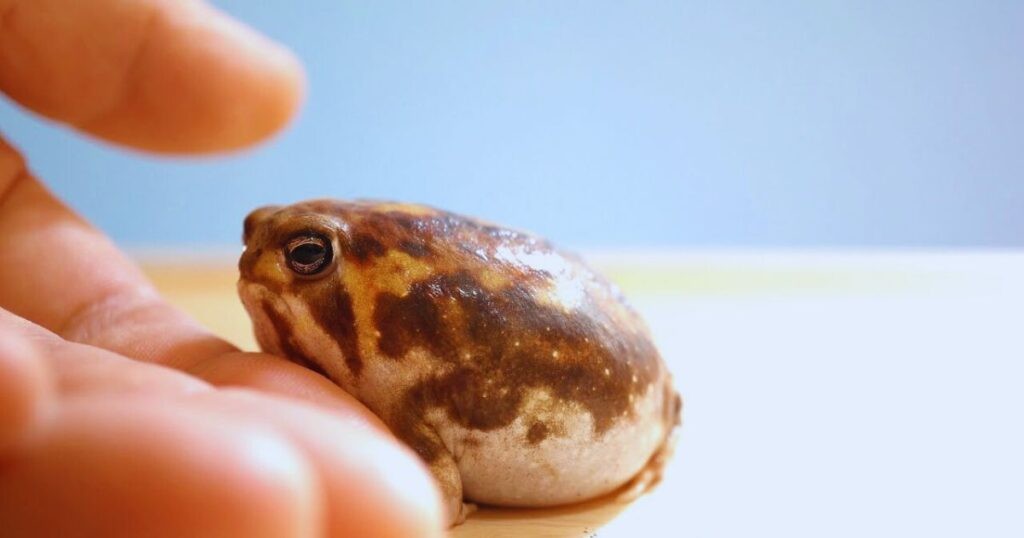
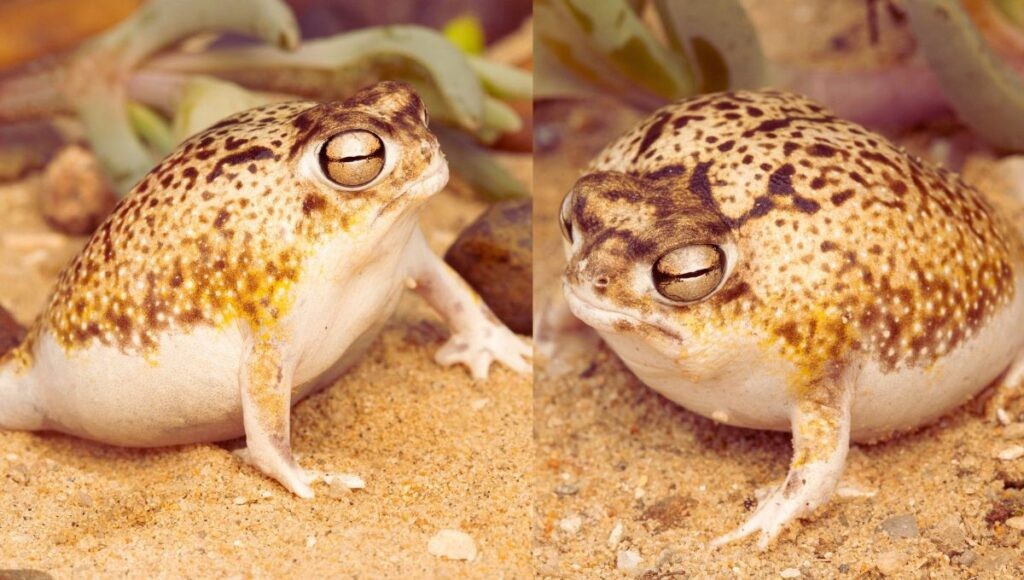
The desert rain frog boasts a unique appearance, characterized by a rounded body, prominent eyes, and a short snout. Its limbs are short, and its feet are spade-like with webbed toes, perfectly adapted for digging and moving through sand. The skin on their underside is remarkably transparent, allowing you to see their internal organs. Adults typically measure between 1.5 to 2.5 inches in length and weigh around 0.39 to 0.49 ounces. Their skin color is yellowish-brown or caramel, which helps them blend seamlessly with their sandy environment.
Unlike many other frog species, desert rain frogs skip the tadpole stage, developing directly from eggs into froglets. Their bulky bodies and short legs prevent them from hopping or leaping; instead, they primarily walk across the sand.
2.2. Geographic Distribution and Natural Habitat
Desert rain frogs are exclusively found in a narrow strip of land, approximately 6 miles wide, along the coasts of Namibia and South Africa. This region is defined by arid dunes with minimal rainfall. The frog’s habitat exemplifies xerophytic vegetation, which is specifically adapted to thrive in dry environments, allowing these frogs to survive in water-scarce conditions.
2.3. Survival Strategies in Arid Conditions
The desert rain frog’s survival hinges on its ability to adapt to arid conditions. They burrow underground to escape the harsh temperatures and conserve moisture. Their transparent skin is capable of absorbing water from the surrounding environment. Fog plays a crucial role by providing essential moisture, and the frogs also obtain hydration from their food.
2.4. Behavioral Patterns
These frogs are nocturnal, spending their days in burrows dug 4 to 8 inches deep in moist soil. They emerge at night to forage on the sandy dunes. Their presence can be identified by small heaps of sand near their burrows. These frogs often leave distinctive footprints around dung patches, where they hunt for insects.
2.5. Are Desert Rain Frogs Poisonous?
Desert rain frogs are non-poisonous and pose no threat to humans or other animals. When threatened, they emit a loud, high-pitched squeak as a defense mechanism.
2.6. Vocalization and Communication
Known for their distinctive high-pitched squeak, often likened to the sound of an angry dog chewing a toy, these frogs are sometimes called “angry rain frogs.” This vocalization is used during mating season and as a defense mechanism when threatened.
2.7. Moisture Conservation Techniques
Living in arid climates, desert rain frogs have transparent skin with specialized glands that retain moisture, keeping them hydrated during dry periods. With rainfall being scarce (around 2 inches annually), fog serves as a vital source of moisture. They also obtain moisture from their diet of small insects and occasional rainfall.
2.8. Breeding and Reproduction
The breeding season typically occurs between June and October. On foggy nights, male frogs emerge from their burrows and use their distinctive squeaking calls to attract females. If a female is receptive, the pair retreats underground to mate. The female lays a clutch of 12 to 40 eggs, which hatch directly into froglets, skipping the tadpole stage. These froglets are immediately capable of moving and hunting small insects on their own.
2.9. Diet and Nutritional Needs
Desert rain frogs are insectivores, feeding primarily on small insect larvae, moths, and beetles. Cannibalism is not observed in this species.
2.10. Predators and Threats
The main predators of desert rain frogs include Cape eagle owls, black eagles, cinnamon-breasted warblers, honey badgers, antelopes, snakes, scorpions, and rodents. They face significant anthropogenic threats, including habitat loss due to opencast diamond mining, road construction, and increasing human settlement.
3. Desert Rain Frog as a Pet: Is It a Good Choice?
3.1. Legality and Ethical Considerations
Before considering a desert rain frog as a pet, ensure it is legal in your area. These frogs are neither dangerous nor poisonous, making them relatively safe to keep.
3.2. Basic Care Requirements
Providing adequate space for burrowing, regulating temperature and humidity, and ensuring a proper diet are essential for their well-being.
3.3. Emotional Bonding
Do not expect emotional bonding with your desert rain frog. They do not form emotional attachments and primarily see their caretakers as food providers.
3.4. Maintenance and Ease of Care
Desert rain frogs are low-maintenance pets, making them suitable for those who can provide a safe and healthy environment. Ensuring they feel secure and stress-free is crucial for their longevity.
4. Purchasing a Desert Rain Frog: Availability and Cost
4.1. Availability
Desert rain frogs are not commonly sold as pets in the Western world but can be found through specialized pet shops or online breeders.
4.2. Price Range
Prices vary depending on availability and location. In the USA, they typically range from $45 to $150. In the UK and other European countries, they may cost between £50 and £120.
5. Comprehensive Guide to Desert Rain Frog Care
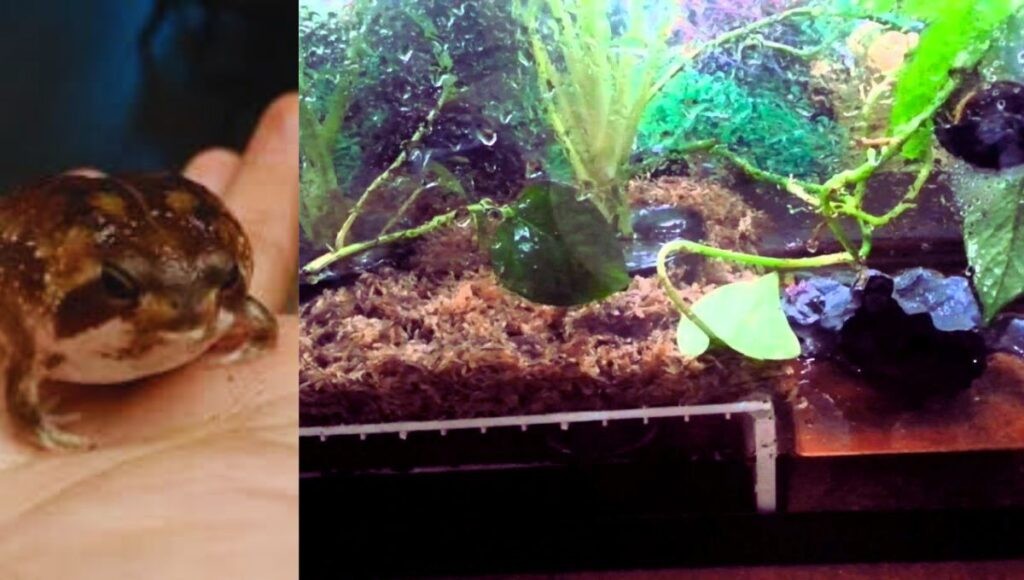
5.1. Setting Up the Habitat
5.1.1. Tank Size
A 10-gallon tank or larger is recommended to provide ample space for your frog.
5.1.2. Substrate
Use a substrate layer at least 4 inches deep, consisting of moist sand or a sand and coconut fiber mixture.
5.1.3. Hiding Places
Include hiding spots such as cork bark, driftwood, or artificial plants to help your frog feel secure.
5.1.4. Water Dish
Provide a shallow dish for drinking and bathing, and clean it daily.
5.2. Temperature and Humidity
5.2.1. Temperature
Maintain a daytime temperature of 75-85°F and a nighttime temperature of 60-70°F.
5.2.2. Humidity
Keep the humidity level between 45% and 60%.
5.2.3. Heating
Use a heat lamp or heat mat to maintain the correct temperature, especially during winter.
5.3. Nutritional Guidelines
5.3.1. Diet
Feed your frog a variety of insects, including crickets, earthworms, mealworms, and waxworms.
5.3.2. Supplements
Dust insects with calcium and vitamin supplements before feeding.
5.3.3. Feeding Frequency
Feed your frog every other day, adjusting the amount based on its size, health, and appetite.
5.3.4. Waste Removal
Remove uneaten food daily to prevent mold and bacteria growth.
5.4. Cleaning and Maintenance
5.4.1. Regular Cleaning
Clean the tank regularly to remove waste food, dead insects, and bacterial substances.
5.4.2. Deep Cleaning
Perform a deep clean of the entire enclosure monthly using a mild disinfectant.
5.4.3. Substrate Replacement
Change the substrate every 10-12 weeks or more frequently if it becomes dirty or smelly.
6. Essential Products for Desert Rain Frog Care
6.1. Recommended Tanks
The Zilla 10 Gallon Pet Reptile Starter Habitat is an excellent choice. It features a transparent view, secure lid, and effective ventilation. It also includes a reflective dome light fixture, heat mat, terrarium liner, and humidity/temperature gauge.
6.2. Decorative Items
PINVNBY Resin Reptile Platform Artificial Tree Trunk is made from eco-friendly, non-toxic resin and provides a safe and attractive hiding spot for your frog.
6.3. Recommended Substrates
Josh’s Frogs BioBedding Tropical Bioactive Substrate is ideal for creating a natural environment where frogs can burrow easily and live plants can thrive.
6.4. Humidity Control
The Reptile Fogger Terrariums Humidifier Fog Machine is adjustable, efficient, and comes with a 1-year warranty.
6.5. Cleaning Supplies
Premium Oxyfresh Terrarium Cleaner is safe, eco-friendly, non-toxic, and effective for eliminating odors.
7. Addressing Common Concerns: FAQs About Desert Rain Frogs
7.1. What Size Tank Does a Desert Rain Frog Need?
A 10-gallon (38-liter) tank is suitable for one desert rain frog.
7.2. How Does a Desert Rain Frog Survive?
They survive by burrowing in moist soil, absorbing moisture through their skin, and obtaining water from fog and their diet.
7.3. Are Desert Rain Frogs Rare?
Yes, they are considered rare, with a limited habitat range along the coastlines of Namibia and South Africa.
7.4. Why Do Desert Rain Frogs Squeak?
They squeak to attract mates during the breeding season and as a defense mechanism when threatened.
7.5. Are Desert Rain Frogs Good Pets?
They can be good pets if you provide the right environment and care, but they do not offer emotional bonding.
7.6. What Does a Desert Rain Frog Eat?
They eat moths, beetles, and insect larvae.
7.7. Do Rain Frogs Jump?
No, desert rain frogs are not built for jumping; they walk on the sand.
7.8. How Long Do Desert Rain Frogs Live?
Their lifespan is typically 3-5 years, but they can live up to 15 years in captivity with proper care.
8. Conservation Status and Environmental Threats
8.1. IUCN Status
Desert rain frogs are listed as “Near Threatened” by the IUCN.
8.2. Threats to Survival
Habitat loss due to diamond mining, road construction, and human settlement are major threats.
8.3. Conservation Efforts
Some regions have banned opencast mining to help restore the frog population, but evidence of restoration is still lacking.
9. Final Thoughts on Desert Rain Frog Care
Desert rain frogs are unique creatures that face numerous threats in their natural habitat. By providing proper care and understanding their needs, you can help ensure their survival and contribute to their conservation. For more information and expert advice on pet care, visit PETS.EDU.VN today.
Call to Action
Want to learn more about desert rain frogs and other amazing pets? Visit pets.edu.vn for detailed guides, expert advice, and the latest information on pet care. Contact us at 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States, or WhatsApp +1 555-987-6543. Let us help you provide the best care for your pets!
