Can I Have A Monkey As A Pet In California? It’s a question many animal lovers ponder, but California law is quite clear. Pets.edu.vn is here to shed light on California’s exotic pet regulations, offering guidance and resources for responsible pet ownership and alternative exotic animal companions allowed in California. Discover more about legal exotic pets and animal welfare regulations with information you can trust.
1. Understanding California’s Exotic Pet Laws
California has some of the strictest laws in the United States regarding exotic pets. Many people are surprised to learn that certain animals, including monkeys, are illegal to keep as pets. The California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) has specific regulations to protect native wildlife and prevent the introduction of potentially harmful species. Let’s explore the specifics of these laws and why they exist.
1.1. Common Illegal Pets in California
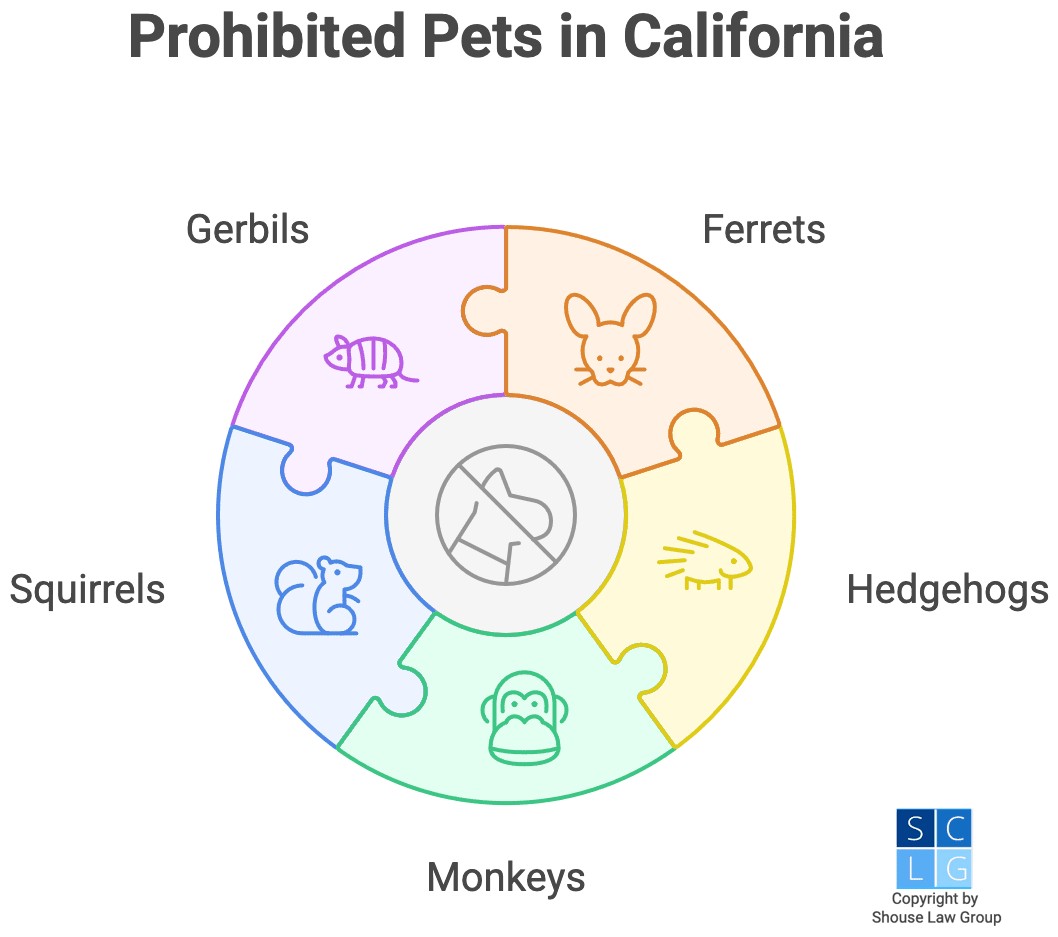
Besides primates, California prohibits owning several other common animals as pets. These include:
- Ferrets
- Hedgehogs
- Squirrels
- Gerbils
These restrictions often surprise people moving to California from other states where these animals are legal. Understanding these laws is crucial for responsible pet ownership and avoiding legal trouble.
1.2. Rationale Behind the Ban
The CDFW’s rationale for banning these animals centers on several key concerns:
- Threat to Native Wildlife: Escaped or abandoned exotic pets can establish feral populations and compete with or prey on native species.
- Source of Predation: Some exotic pets can directly prey on native fish and wildlife, disrupting the natural ecosystem.
- Disease Transmission: Exotic animals can carry diseases that may not affect them but can be devastating to native populations or even humans.
For example, ferrets are banned due to concerns that they could establish a feral population and threaten native wildlife. Hedgehogs and gerbils are considered potential sources of predation and disease transmission.
1.3. Additional Prohibited Animals
Beyond the commonly known restrictions, California law also prohibits owning a wide range of other animals, including:
- Monk or Quaker parakeets
- Crows
- Skunks
- Parrots (certain species)
- Lemurs
- Chimpanzees
- Non-domesticated chinchillas
- Hamsters (other than domesticated races of golden or dwarf hamsters)
- Sugar gliders
- Raccoons
- Otters
Additionally, local jurisdictions may have their own bans on certain animals. For example, many cities have restrictions on owning pit bulls that have not been spayed or neutered.
1.4. Importance for Visitors
It’s important for visitors to California to be aware of these regulations. Bringing a prohibited animal into the state, even temporarily, can result in legal penalties. The CDFW requires a Restricted Species Permit for anyone importing, exporting, or possessing a restricted animal. These permits are issued for limited purposes and involve stringent requirements. Even a recreational vehicle trip to California is not a valid reason for obtaining such a permit.
2. Why Monkeys are Illegal Pets in California
Monkeys, as primates, are subject to strict regulations in California due to public safety and conservation concerns. Keeping a monkey as a pet raises various ethical and practical issues. Let’s delve into the specific reasons behind the prohibition.
2.1. Public Safety Concerns
Monkeys can be unpredictable and potentially dangerous, especially as they mature. They possess sharp teeth and strong muscles, capable of inflicting serious injuries. Even seemingly docile monkeys can bite or scratch if they feel threatened or stressed.
- Bites and Scratches: Monkey bites can transmit diseases like herpes B virus, which can be fatal to humans.
- Aggression: Monkeys may exhibit aggressive behavior, especially during mating season or when defending their territory.
- Unpredictability: Monkeys can be unpredictable, making it difficult to ensure the safety of people around them, especially children.
2.2. Zoonotic Diseases
Monkeys can carry various zoonotic diseases transmissible to humans. These diseases can pose significant health risks, and some can be life-threatening.
- Herpes B Virus: As mentioned earlier, this virus is particularly dangerous and can cause severe neurological damage or death.
- Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV): While not directly transmissible to humans, SIV is closely related to HIV and raises concerns about potential mutations.
- Monkeypox: Although less common, monkeypox is another zoonotic disease that can cause fever, rash, and other symptoms in humans.
- Parasites: Monkeys can also carry various parasites that can infect humans, such as intestinal worms and protozoa.
2.3. Conservation Issues
Many monkey species are endangered or threatened in the wild. The demand for monkeys as pets can contribute to the illegal wildlife trade, further endangering these populations.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade: The capture and trade of wild monkeys can decimate local populations and disrupt ecosystems.
- Habitat Loss: Habitat destruction also threatens monkey populations, and the pet trade exacerbates this issue.
- Ethical Considerations: Keeping monkeys as pets deprives them of their natural social structures and environments, raising ethical concerns about animal welfare.
2.4. Welfare of the Animal
Monkeys have complex social and behavioral needs that are difficult to meet in a typical household environment. They require specialized care, including:
- Social Interaction: Monkeys are highly social animals and need to live in groups with other monkeys to thrive.
- Enrichment: They require mental stimulation and physical activity to prevent boredom and destructive behaviors.
- Specialized Diet: Monkeys need a varied and balanced diet that mimics their natural food sources.
- Veterinary Care: They require specialized veterinary care, as many common pet medications are not safe for monkeys.
Providing adequate care for a monkey is often beyond the capabilities of most pet owners, leading to suffering and neglect.
3. Dangerous Animals Illegal in California
California law also prohibits keeping certain dangerous animals as pets to protect public safety. This includes a variety of predators and other potentially harmful species.
3.1. List of Dangerous Animals
The list of dangerous animals that cannot be kept as pets in California includes:
- Foxes
- Coyotes
- Lions
- Tigers
- Leopards
- Cheetahs
- Bears
- Bobcats
- Hawks
- Wolves and wolf hybrids
- Crocodiles and alligators
- Vipers
These animals pose a clear threat to public safety due to their size, strength, and predatory instincts.
3.2. Other Restricted Animals
In addition to the explicitly dangerous animals, other animals are restricted due to various concerns. These include:
- Zebras
- Certain non-native snails
- Lemurs
- Other primates (including monkeys)
These restrictions are based on factors such as potential ecological impact, disease transmission, and the welfare of the animals themselves.
4. Endangered Animals and Pet Ownership
California law also prohibits owning endangered or nearly endangered animals as pets. This is to protect these vulnerable species and prevent further decline in their populations.
4.1. Examples of Endangered Animals
Examples of endangered animals that cannot be kept as pets in California include:
- Jaguars
- Pandas
- Elephants
These animals are protected under state and federal laws, and owning them as pets is strictly prohibited.
5. Exceptions to the Rule: Permits
While owning most of these animals is illegal in California, there are exceptions. The only way to legally own a restricted animal is by obtaining a permit from the CDFW.
5.1. Types of Permits Available
The CDFW offers various permits depending on the intended purpose of owning the animal. These include permits for:
- Research
- Running a shelter
- Exhibition (at a single event, zoo, or aquarium)
- Breeding
- Aquaculture
- Animal care
Each type of permit has specific requirements and restrictions.
5.2. Costs and Requirements
Obtaining a permit can be a costly and complex process. The costs include:
- Application and inspection fees (over $450 for new permits)
- Annual renewal fees (nearly $400)
- Permit fees
In addition to the fees, applicants must demonstrate that they have the experience and ability to care for the exotic animal. They must also meet specific requirements related to housing, feeding, and veterinary care.
5.3. Animal Care Permits
Most pet owners would attempt to apply for a permit for animal care. The cost of this permit depends on whether the animal is designated as a:
- Detrimental animal: An animal that poses a threat to native species, the local ecosystem, agriculture, or public health and safety.
- Welfare animal: An animal that is banned to prevent the depletion of wild populations.
Obtaining a permit for a detrimental animal is generally more difficult and expensive due to the greater risks involved.
6. Penalties for Violating California’s Exotic Pet Laws
Keeping an illegal animal as a pet in California is a crime punishable as a misdemeanor. The penalties can be severe.
6.1. Criminal Penalties
The criminal penalties for violating California’s exotic pet laws include:
- Up to 6 months in jail
- A fine of between $500 and $10,000
The severity of the penalties depends on the type of animal involved and the circumstances of the violation.
6.2. Financial Penalties
In addition to criminal fines, individuals who violate these laws may also be required to pay the costs associated with:
- The investigation
- Attorneys’ fees
- Expert witness fees
- Caring for the animal for at least 30 days
- Transporting the animal out of California
- Euthanizing the animal
These costs can quickly add up to a substantial financial burden.
6.3. Animal Seizure
Perhaps the most heartbreaking consequence of violating these laws is the seizure of the illegal pet. The animal will be taken from the owner and either transported out of state or euthanized, depending on its species and condition.
6.4. Prosecution Rates
Although the penalties for violating California’s exotic pet laws are severe, prosecutions are relatively rare. However, this does not mean that these laws should be taken lightly. The risk of being caught and facing the consequences is always present.
7. Legal Exotic Pets in California
While many animals are prohibited, some exotic animals are legal to own in California with proper permits and adherence to regulations. Here are some examples:
7.1. Certain Reptiles and Amphibians
Many non-venomous reptiles and amphibians are legal to own in California, such as:
- Bearded dragons
- Leopard geckos
- Ball pythons
- Corn snakes
- Pacman frogs
However, it is important to research specific species and local regulations to ensure compliance. Some reptiles, like certain large snakes or venomous species, may still be prohibited.
7.2. Some Birds
Certain domesticated bird species can be kept as pets, including:
- Cockatiels
- Parakeets (Budgies)
- Finches
- Canaries
However, restrictions may apply to certain wild or non-native bird species. Always check with the CDFW for clarification.
7.3. Domesticated Animals
Many domesticated animals are legal to own in California, such as:
- Dogs
- Cats
- Rabbits
- Guinea pigs
- Domesticated rats and mice
These animals are generally subject to local regulations regarding licensing, vaccinations, and animal welfare.
8. Responsible Pet Ownership in California
Whether you own a legal exotic pet or a more common domesticated animal, responsible pet ownership is essential. This includes:
8.1. Researching the Animal’s Needs
Before acquiring any pet, thoroughly research its specific needs, including:
- Diet
- Housing
- Social interaction
- Enrichment
- Veterinary care
Ensure that you can provide adequate care for the animal throughout its lifetime.
8.2. Providing Proper Care
Proper care includes:
- Feeding a balanced and appropriate diet
- Providing a clean and safe environment
- Ensuring adequate exercise and mental stimulation
- Regular veterinary checkups and vaccinations
- Socialization and training
8.3. Complying with Local Regulations
Be aware of and comply with all local regulations regarding pet ownership, including:
- Licensing
- Vaccinations
- Leash laws
- Noise ordinances
- Restrictions on certain breeds or species
8.4. Preventing Escapes
Take steps to prevent your pet from escaping and becoming a threat to the environment or public safety. This includes:
- Secure enclosures
- Proper leash control
- Microchipping
- Identification tags
8.5. Considering Adoption
Consider adopting a pet from a local shelter or rescue organization. Many animals need loving homes, and adoption can be a rewarding experience.
9. Alternatives to Owning a Monkey
If you’re drawn to primates, but can’t legally own a monkey in California, consider these alternatives:
9.1. Volunteering at a Primate Sanctuary
Many primate sanctuaries exist throughout the United States. These sanctuaries provide care for rescued primates and often rely on volunteers. Volunteering can allow you to interact with primates in a responsible and ethical manner.
9.2. Supporting Conservation Organizations
Support organizations dedicated to primate conservation. Your donations can help protect primate habitats and combat the illegal wildlife trade.
9.3. Learning About Primates
Educate yourself about primates. Learn about their behavior, ecology, and conservation status. This knowledge can help you appreciate these animals and support their protection.
9.4. Virtual Interactions
Enjoy primates through documentaries, online videos, and virtual reality experiences. These options allow you to appreciate primates without contributing to the demand for them as pets.
10. How PETS.EDU.VN Can Help
Navigating exotic pet laws and responsible pet ownership can be challenging. That’s where PETS.EDU.VN comes in. We offer a wealth of information and resources to help you make informed decisions about pet ownership.
10.1. Comprehensive Information
PETS.EDU.VN provides comprehensive information on:
- Exotic pet laws in California and other states
- The needs of various exotic animals
- Responsible pet ownership practices
- Alternatives to owning exotic pets
- Animal welfare and conservation issues
10.2. Expert Advice
Our team of experts includes veterinarians, animal behaviorists, and legal professionals. We provide accurate and up-to-date information you can trust.
10.3. Community Forum
Connect with other pet owners in our community forum. Share your experiences, ask questions, and learn from others.
10.4. Service Directory
Find local veterinarians, pet stores, and other services in our directory. We only list reputable and ethical businesses that prioritize animal welfare.
11. The Importance of E-E-A-T and YMYL
In the realm of online content, E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) and YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) are critical concepts, especially when discussing topics like pet ownership and animal welfare. These guidelines, used by Google to evaluate content quality, ensure that the information presented is reliable, accurate, and safe for users.
11.1. Understanding E-E-A-T
- Experience: Content should reflect real-world experience. In the context of pet ownership, this means drawing on personal experiences or insights from those with direct involvement in animal care.
- Expertise: The content should demonstrate a high level of knowledge on the topic. This can be achieved by consulting with veterinarians, animal behaviorists, and other qualified professionals.
- Authoritativeness: The source of the information should be recognized as an authority in its field. This can be established through citations of reputable sources and endorsements from other experts.
- Trustworthiness: The content should be accurate, honest, and unbiased. This can be ensured through fact-checking, transparency about sources, and a commitment to presenting all sides of an issue.
11.2. YMYL Considerations
YMYL topics are those that can directly impact a person’s health, safety, financial stability, or well-being. Pet ownership falls under this category because decisions about pet care can have significant consequences for both the animal and the owner.
For YMYL topics, it’s especially important to:
- Provide accurate and up-to-date information.
- Cite reputable sources, such as veterinary journals, government agencies, and animal welfare organizations.
- Avoid making unsubstantiated claims or giving medical advice without proper qualifications.
- Be transparent about potential risks and benefits.
11.3. Applying E-E-A-T and YMYL to Pet Ownership Content
When creating content about pet ownership, consider the following:
- Consult with experts: Interview veterinarians, animal behaviorists, and other professionals to ensure accuracy.
- Cite reputable sources: Back up claims with evidence from scientific studies, government publications, and animal welfare organizations.
- Share personal experiences: Offer insights based on your own experiences with pet ownership, but be clear about the limitations of anecdotal evidence.
- Be transparent: Disclose any potential conflicts of interest and be open about your sources and methods.
- Prioritize accuracy: Fact-check all information carefully and correct any errors promptly.
- Focus on safety: Provide guidance on safe handling, feeding, and care practices.
- Promote responsible pet ownership: Encourage readers to adopt pets from shelters, spay or neuter their animals, and provide them with proper care.
By adhering to E-E-A-T and YMYL guidelines, you can create content that is not only informative but also trustworthy and beneficial for your audience.
12. Statistics and Trends in Pet Ownership
Understanding the latest statistics and trends in pet ownership can help you make informed decisions about pet care and advocacy. Here are some key insights:
12.1. Pet Ownership Demographics
- Overall Pet Ownership: According to the American Pet Products Association (APPA), approximately 70% of U.S. households own a pet.
- Dog Ownership: Dogs are the most popular pet, with approximately 63.4 million households owning at least one dog.
- Cat Ownership: Cats are the second most popular pet, with approximately 42.7 million households owning at least one cat.
- Other Pets: Other popular pets include fish, birds, reptiles, and small mammals.
- Age Demographics: Pet ownership is most common among younger and middle-aged adults, with the highest rates among those aged 35-44.
- Income Demographics: Pet ownership is more common among higher-income households.
12.2. Spending on Pets
- Overall Spending: Americans spend billions of dollars on their pets each year. In 2023, total pet industry expenditures were estimated at $143.6 billion.
- Food: Pet food is the largest expense, accounting for approximately $62.7 billion in 2023.
- Veterinary Care: Veterinary care is the second largest expense, accounting for approximately $37 billion in 2023.
- Supplies, Medicine, and Other Services: Other expenses include pet supplies, over-the-counter medications, grooming, boarding, and training.
12.3. Trends in Pet Ownership
- Humanization of Pets: Pets are increasingly viewed as members of the family, leading to increased spending on premium food, healthcare, and accessories.
- Adoption from Shelters: Adoption from animal shelters and rescue organizations is becoming more popular, driven by increased awareness of animal welfare issues.
- Exotic Pet Ownership: While many exotic animals are illegal, some individuals are drawn to owning unique and unusual pets. This trend raises concerns about animal welfare and conservation.
- Online Pet Services: Online services such as telemedicine, pet food delivery, and pet product subscriptions are becoming increasingly popular.
12.4. Responsible Pet Ownership Statistics
- Spay/Neuter Rates: Spay/neuter rates are relatively high among pet owners in the United States, but there is still room for improvement.
- Microchipping Rates: Microchipping is becoming more common, but many pets are still not microchipped.
- Vaccination Rates: Vaccination rates are generally high, but some pets are not fully vaccinated.
- Pet Insurance Coverage: Pet insurance coverage is increasing, but still relatively low compared to other types of insurance.
12.5. Charts for Pet Ownership
| Statistic | Data |
|---|---|
| Percentage of U.S. Households Owning a Pet | 70% |
| Number of Households Owning a Dog | 63.4 million |
| Number of Households Owning a Cat | 42.7 million |
| Total Pet Industry Expenditures (2023) | $143.6 billion |
| Spending on Pet Food (2023) | $62.7 billion |
| Spending on Veterinary Care (2023) | $37 billion |

By staying informed about these statistics and trends, you can make more informed decisions about pet ownership and advocate for responsible pet care practices.
13. Recent Updates and Advancements in Pet Care
The field of pet care is constantly evolving, with new advancements in nutrition, medicine, and technology. Staying up-to-date on these developments can help you provide the best possible care for your pets.
13.1. Advancements in Pet Nutrition
- Personalized Diets: Companies are now offering personalized diets based on a pet’s age, breed, weight, activity level, and health conditions.
- Grain-Free and Limited Ingredient Diets: Grain-free and limited ingredient diets are becoming more popular among pet owners who are concerned about allergies and sensitivities.
- Raw Food Diets: Raw food diets are gaining traction, with proponents claiming that they offer numerous health benefits. However, it is important to consult with a veterinarian before switching to a raw food diet.
- Supplements: Supplements such as probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, and glucosamine are increasingly being used to support pet health.
13.2. Advances in Veterinary Medicine
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Minimally invasive surgical techniques are becoming more common, offering benefits such as reduced pain, shorter recovery times, and smaller incisions.
- Advanced Imaging: Advanced imaging technologies such as MRI and CT scans are allowing veterinarians to diagnose and treat conditions more accurately.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell therapy is being used to treat a variety of conditions in pets, including arthritis, hip dysplasia, and spinal cord injuries.
- Cancer Treatment: New cancer treatments such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy are showing promise in improving outcomes for pets with cancer.
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine is becoming more accessible, allowing pet owners to consult with veterinarians remotely.
13.3. Technological Innovations
- Wearable Technology: Wearable technology such as activity trackers and GPS collars are helping pet owners monitor their pet’s health and safety.
- Smart Feeders: Smart feeders can dispense food automatically and monitor a pet’s eating habits.
- Automated Litter Boxes: Automated litter boxes can clean themselves automatically, reducing the hassle of litter box maintenance.
- Interactive Toys: Interactive toys can provide mental stimulation and entertainment for pets.
13.4. Table of Updates and Advancements
| Category | Advancement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pet Nutrition | Personalized diets | Tailored to meet specific nutritional needs, addressing allergies, sensitivities, and health conditions. |
| Veterinary Medicine | Minimally invasive surgery | Reduced pain, shorter recovery times, smaller incisions, and decreased risk of complications. |
| Technology | Wearable technology (activity trackers) | Monitoring of pet’s activity levels, sleep patterns, and overall health. Early detection of potential health issues. |
| General Care | Telemedicine | Convenient access to veterinary advice, especially for routine check-ups or non-emergency situations. Reduced travel time and stress for both pet and owner. |
13.5. Important Considerations
- Consult with Your Veterinarian: Always consult with your veterinarian before making any changes to your pet’s diet, treatment plan, or care routine.
- Research Products and Services: Research products and services carefully before purchasing them. Read reviews, compare prices, and check for safety certifications.
- Be Skeptical of Unproven Claims: Be skeptical of unproven claims about pet products and services. Look for scientific evidence to support any claims.
- Prioritize Safety: Prioritize safety when choosing pet products and services. Make sure that products are non-toxic and that services are provided by qualified professionals.
By staying informed about these updates and advancements, you can make informed decisions about how to best care for your pets and ensure their health and well-being.
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about owning exotic pets in California:
14.1. Is it legal to own a monkey in California?
No, it is illegal to own a monkey as a pet in California. Monkeys are classified as restricted animals and are prohibited due to public safety, animal welfare, and conservation concerns.
14.2. What other animals are illegal to own in California?
Besides monkeys, other animals that are illegal to own in California include ferrets, hedgehogs, squirrels, gerbils, foxes, coyotes, lions, tigers, leopards, cheetahs, bears, bobcats, hawks, wolves and wolf hybrids, crocodiles and alligators, and vipers.
14.3. Can I get a permit to own a restricted animal in California?
Yes, you can get a permit to own a restricted animal in California, but only for specific purposes such as research, exhibition, or animal care. The requirements are stringent, and the costs can be high.
14.4. What are the penalties for owning an illegal pet in California?
The penalties for owning an illegal pet in California include up to 6 months in jail and a fine of between $500 and $10,000. You may also be required to pay the costs associated with the investigation, caring for the animal, and transporting or euthanizing the animal.
14.5. What exotic animals are legal to own in California?
Some exotic animals that are legal to own in California include certain reptiles and amphibians (such as bearded dragons and ball pythons), some birds (such as cockatiels and parakeets), and domesticated animals (such as dogs and cats).
14.6. How can I find out if an animal is legal to own in California?
You can contact the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) or visit their website for a list of restricted animals and permit requirements.
14.7. What should I do if I see someone owning an illegal pet in California?
You should report the incident to the CDFW. Provide as much information as possible, including the type of animal, the location, and the owner’s contact information.
14.8. What are the ethical concerns about owning exotic pets?
Ethical concerns about owning exotic pets include the welfare of the animals, the potential for harm to public safety and the environment, and the impact on conservation efforts.
14.9. What are some alternatives to owning a monkey?
Alternatives to owning a monkey include volunteering at a primate sanctuary, supporting conservation organizations, learning about primates, and enjoying them through documentaries and virtual reality experiences.
14.10. Where can I find more information about responsible pet ownership in California?
You can find more information about responsible pet ownership in California on the PETS.EDU.VN website. We provide comprehensive information on pet care, local regulations, and animal welfare issues.
Conclusion
While the idea of owning a monkey as a pet may be appealing to some, California law is clear: it is illegal. This prohibition is in place to protect public safety, animal welfare, and the environment. However, there are many other legal and rewarding ways to interact with animals and enjoy the benefits of pet ownership. Remember, responsible pet ownership starts with understanding the laws and regulations in your area and providing proper care for your animal.
Ready to learn more about responsible pet ownership and discover the perfect animal companion for your lifestyle? Visit pets.edu.vn today for a wealth of information, expert advice, and a supportive community. Contact us at 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-987-6543. Your journey to responsible and fulfilling pet ownership starts here, including guidance on restricted species permits, alternative animal companions, and local animal control regulations.
