Navigating the world of pet nutrition can be confusing, especially when it comes to understanding the safety and suitability of pet food for human consumption. At PETS.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing clear, reliable information to help you make the best decisions for your furry friends, and to address common queries like whether fresh pet food is safe for humans to eat.
1. Understanding Pet Food Regulations and Standards
Pet food regulations and standards are in place to ensure the safety and nutritional adequacy of food products intended for animal consumption. These regulations vary by country and region, but they generally cover aspects such as ingredient sourcing, manufacturing processes, labeling requirements, and quality control measures.
1.1. Regulatory Bodies Governing Pet Food
- United States: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates pet food at the federal level, while state agencies enforce regulations at the local level. The Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) provides guidelines for pet food formulation and labeling.
- European Union: The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) provides scientific advice and risk assessments related to food and feed safety. EU regulations cover aspects such as animal health, hygiene, and feed additives.
- Canada: The Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) regulates pet food in Canada, ensuring compliance with safety standards and labeling requirements.
1.2. Key Differences Between Human Food and Pet Food Regulations
While both human food and pet food are subject to regulatory oversight, there are some key differences in the standards and requirements that apply to each category:
| Feature | Human Food | Pet Food |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Sourcing | Ingredients must meet human consumption standards and be sourced from approved suppliers. | Ingredients may include by-products and feed-grade components not suitable for human consumption. |
| Manufacturing Standards | Facilities must adhere to strict hygiene and sanitation standards to prevent contamination. | Manufacturing standards may be less stringent than those for human food, with fewer requirements for hygiene and sanitation. |
| Labeling Requirements | Labels must provide detailed information about ingredients, nutritional content, and allergen warnings. | Labels must include information about ingredients, guaranteed analysis, and feeding guidelines, but may not be as detailed as human food labels. |
| Quality Control | Rigorous testing and inspection procedures are in place to ensure product safety and quality. | Quality control measures may be less comprehensive than those for human food, with fewer requirements for testing and inspection. |
| Intended Use | Human food is intended for human consumption and must meet specific nutritional and safety standards. | Pet food is intended for animal consumption and must meet nutritional requirements for specific animal species and life stages. |
| Manufacturing Location | 100% human edible ingredients (including supplements) and requires the pet food to be manufactured in a licensed food facility per federal/state food safety standards | Pet foods are NOT manufactured in a licensed food facility. |
Understanding these regulatory distinctions is crucial for assessing the safety and suitability of pet food for human consumption.
2. Examining Freshpet and Its Marketing Claims
Freshpet is a popular brand of refrigerated pet food that markets itself as a healthier, more natural alternative to traditional dry kibble. The company emphasizes the use of fresh, whole ingredients in its recipes and promotes the idea that its food is similar in quality to human food.
2.1. Overview of Freshpet Products
Freshpet offers a variety of pet food products for dogs and cats, including:
- Freshpet Select: Recipes made with real meat, vegetables, and grains.
- Freshpet Vital: Grain-free recipes with limited ingredients.
- Freshpet Deli Fresh: Soft, moist recipes with a focus on palatability.
These products are typically sold in refrigerated cases in pet stores and supermarkets.
2.2. Analysis of Marketing Messages
Freshpet’s marketing often blurs the lines between pet food and human food, using language and imagery that suggest its products are of the same quality as what humans consume. For example, the company’s website and advertisements may feature phrases such as “real ingredients,” “freshly made,” and “kitchen-crafted recipes.”
The brand’s marketing seems to be claiming their pet foods are exactly the same as human food.
2.3. Expert Opinions on Freshpet’s Claims
While Freshpet’s marketing may appeal to pet owners looking for healthier options, it’s important to critically evaluate the company’s claims. Pet nutrition experts and consumer advocates have raised concerns about whether Freshpet’s marketing is misleading or deceptive.
Susan Thixton, a pet food safety advocate and author of “Buyer Beware,” has questioned whether Freshpet’s products meet the legal requirements of human-grade pet food. She notes that human-grade pet food requires 100% human-edible ingredients and must be manufactured in a licensed food facility, which may not be the case for Freshpet.
Here at PETS.EDU.VN we believe in transparency and want to share all available data with you so you can make the best informed decisions.
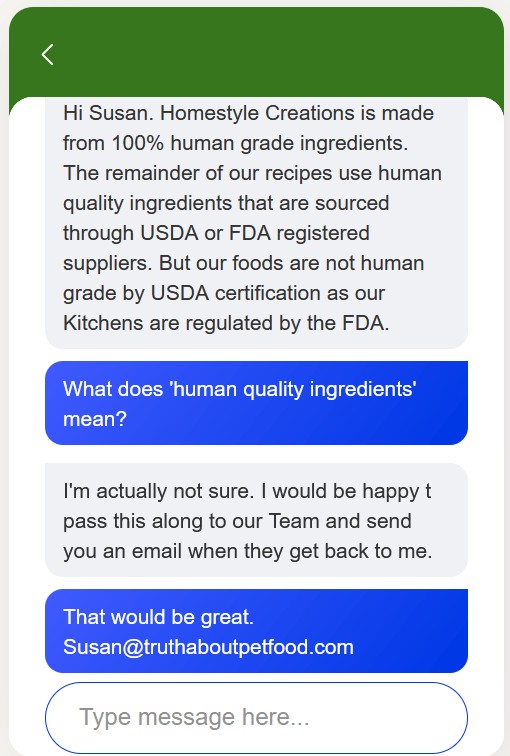 Freshpet Conversation
Freshpet Conversation
3. Can Humans Eat Freshpet? Assessing the Risks
While Freshpet may appear to be a wholesome and nutritious option for pets, it’s essential to consider the potential risks associated with human consumption.
3.1. Ingredient Quality and Sourcing
Freshpet’s ingredients may include components that are not considered safe or suitable for human consumption. Even if the ingredients are sourced from USDA- or FDA-registered suppliers, they may not be of the same quality as those used in human food.
Freshpet admitted their pet products are not human grade, they are not manufactured in a licensed human food facility. They are feed grade.
3.2. Manufacturing Processes and Hygiene Standards
Pet food manufacturing facilities are typically held to lower hygiene standards than human food facilities. This means that Freshpet products may be exposed to contaminants or pathogens that could pose a health risk to humans.
3.3. Potential Health Hazards
Consuming Freshpet could expose humans to a variety of health hazards, including:
- Bacterial contamination: Pet food may contain harmful bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, which can cause food poisoning in humans.
- Parasites: Pet food may be contaminated with parasites or parasite eggs, which can cause intestinal infections in humans.
- Chemical contaminants: Pet food may contain chemical contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, and toxins, which can have adverse health effects.
- Nutritional imbalances: Pet food is formulated to meet the specific nutritional needs of animals, and it may not provide the right balance of nutrients for humans.
3.4. Case Studies and Research Findings
Several studies have investigated the safety of pet food for human consumption. One study published in the “Journal of Food Protection” found that a significant percentage of pet food samples tested positive for Salmonella and other pathogens.
Another study published in the “Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association” found that pet food recalls due to contamination have increased in recent years, highlighting the potential risks associated with pet food consumption.
4. Comparing Human Food and Pet Food Manufacturing Standards
Understanding the differences between human food and pet food manufacturing standards is crucial for assessing the safety of pet food for human consumption.
4.1. USDA Regulations for Human Food
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) regulates the production and processing of meat, poultry, and egg products for human consumption. USDA regulations cover aspects such as:
- Inspection: USDA inspectors are present in food processing facilities to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Sanitation: Facilities must meet strict sanitation requirements to prevent contamination.
- HACCP: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems are in place to identify and control potential hazards.
- Labeling: Labels must provide accurate and informative information about the product.
For food products that contain more than 3% meat (which includes human grade pet foods), a USDA inspector is required by law to be onsite during all hours of operation. The USDA’s role is to assure all safety standards are followed; ingredients are human edible and stored under refrigeration, manufacturing conditions are clean.
4.2. FDA Regulations for Pet Food
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates pet food at the federal level, but the standards are generally less stringent than those for human food. FDA regulations for pet food cover aspects such as:
- Ingredient standards: Ingredients must be safe and suitable for animal consumption, but they do not necessarily have to meet human food standards.
- Labeling requirements: Labels must provide information about ingredients, guaranteed analysis, and feeding guidelines.
- Manufacturing practices: Facilities must follow good manufacturing practices (GMPs) to ensure product safety and quality.
Feed grade pet foods are NOT held to the same standards. No USDA representative is onsite to assure human edible ingredients, proper storage of ingredients and clean manufacturing conditions.
4.3. Examples of Deficiencies in Pet Food Manufacturing
Several examples of deficiencies in pet food manufacturing have been documented, highlighting the potential risks associated with pet food consumption.
Through Freedom of Information Act we acquired the FDA inspection report of a Mars Petcare feed grade pet food facility. The inspection report stated:
“Inspectional Observations
- Failure to inspect, segregate, or otherwise handle raw materials and ingredients used in manufacturing under conditions that will protect the animal food against contamination and minimize deterioration.
- Failure to take effective measures to exclude pests from your plant and protect against contamination of animal food by pests (Discussion Item from 10/27/2016 EI).”
The inspection report also stated employees of this feed grade pet food plant documented that “millions of roaches” infested the food production area.
Even though this feed grade pet food facility did not protect ingredients from contamination and deterioration, and even though there was a roach infestation in the food production area – there was no recall, no warning letter issued. Why? Because this was/is acceptable manufacturing conditions for a feed.
4.4. Implications for Human Health
The lower manufacturing standards for pet food have significant implications for human health. Consuming pet food could expose humans to contaminants, pathogens, and other hazards that are not typically found in human food.
5. Addressing the “Feed Grade” vs. “Human Grade” Distinction
The distinction between “feed grade” and “human grade” ingredients and manufacturing processes is critical for understanding the safety of pet food for human consumption.
5.1. Defining “Feed Grade” and “Human Grade”
- Feed grade: Ingredients and manufacturing processes that meet the minimum standards for animal feed but may not be suitable for human consumption.
- Human grade: Ingredients and manufacturing processes that meet the standards for human food and are considered safe and suitable for human consumption.
5.2. Legal Requirements for “Human Grade” Pet Food
To be labeled as “human grade,” pet food must meet strict legal requirements, including:
- All ingredients must be human-edible and sourced from approved suppliers.
- The food must be manufactured in a facility that is licensed to produce human food.
- The facility must adhere to strict hygiene and sanitation standards.
5.3. Implications of Using “Feed Grade” Ingredients
Using “feed grade” ingredients in pet food can have several implications for human health:
- The ingredients may be of lower quality than those used in human food.
- The ingredients may be contaminated with pathogens or toxins.
- The ingredients may not provide the right balance of nutrients for humans.
5.4. Consumer Perception and Misconceptions
Many consumers mistakenly believe that pet food is held to the same standards as human food. This misconception can lead to unsafe practices such as feeding pet food to children or elderly individuals.
6. Exploring Alternative Perspectives and Arguments
While the consensus among experts is that pet food is not safe for human consumption, there are some alternative perspectives and arguments to consider.
6.1. Arguments in Favor of Pet Food Safety
Some argue that pet food is becoming increasingly safe due to improved manufacturing practices and stricter regulations. They point to the fact that many pet food companies now use high-quality ingredients and follow rigorous quality control procedures.
6.2. Counterarguments and Rebuttals
However, these arguments are often countered by the fact that pet food regulations are still less stringent than those for human food, and that pet food contamination remains a significant concern.
6.3. Ethical Considerations
Some argue that it is unethical to waste perfectly good pet food, especially in situations where humans are facing food shortages. However, this argument fails to address the potential health risks associated with consuming pet food.
6.4. Situational Contexts
In emergency situations where human food is not available, some people may consider consuming pet food as a last resort. However, this should only be done after carefully weighing the potential risks and benefits.
7. Practical Guidelines and Recommendations
To ensure your safety and the safety of your family, it’s important to follow these practical guidelines and recommendations:
7.1. Safe Handling Practices for Pet Food
- Always wash your hands thoroughly after handling pet food.
- Avoid touching your face or mouth while handling pet food.
- Store pet food in a separate area from human food.
- Clean and disinfect pet food bowls and utensils regularly.
7.2. Storage and Preparation Tips
- Store pet food in a cool, dry place to prevent spoilage.
- Do not store pet food in the refrigerator next to human food.
- Do not cook or heat pet food before serving it to your pet.
7.3. Alternatives to Pet Food for Human Consumption
- If you are facing food shortages, contact your local food bank or emergency services.
- Consider growing your own food or purchasing from local farmers.
- Stock up on non-perishable human food items for emergency situations.
7.4. Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
If you have consumed pet food and are experiencing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, consult with a healthcare professional immediately.
8. Examining Pet Food Recalls and Contamination Incidents
Pet food recalls and contamination incidents serve as a reminder of the potential risks associated with pet food consumption.
8.1. Notable Pet Food Recalls in Recent Years
Several notable pet food recalls have occurred in recent years due to contamination with Salmonella, melamine, and other harmful substances.
8.2. Causes of Contamination
Pet food contamination can occur due to a variety of factors, including:
- Poor hygiene practices in manufacturing facilities.
- Use of contaminated ingredients.
- Inadequate testing and quality control procedures.
- Packaging defects.
8.3. Impact on Pet and Human Health
Pet food contamination can have serious consequences for both pet and human health, leading to illness, hospitalization, and even death.
8.4. Prevention Strategies
To prevent pet food contamination, it’s important to:
- Choose reputable brands that follow strict quality control procedures.
- Store and handle pet food properly.
- Stay informed about pet food recalls and contamination incidents.
- Report any suspected contamination to the appropriate authorities.
9. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Pet Food
Many misconceptions exist regarding pet food, leading to confusion and potentially unsafe practices.
9.1. “Pet Food is Just as Safe as Human Food”
This is a common misconception. As we’ve outlined in this article, pet food regulations are generally less stringent than those for human food, and pet food may contain ingredients and contaminants that are not considered safe for human consumption.
9.2. “If My Pet Eats It, It Must Be Safe for Humans Too”
This is another dangerous misconception. Pets have different nutritional needs and tolerances than humans, and what is safe for them may not be safe for us.
9.3. “All Pet Food is Created Equal”
Not all pet food is created equal. The quality of ingredients, manufacturing processes, and quality control procedures can vary widely between brands.
9.4. “Pet Food is Only Made from Scraps and Leftovers”
While some pet food may contain by-products, many brands now use high-quality ingredients and follow rigorous manufacturing practices.
10. Future Trends and Innovations in Pet Food
The pet food industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time.
10.1. Humanization of Pet Food
One of the biggest trends in the pet food industry is the humanization of pet food, with companies increasingly marketing their products as similar in quality and ingredients to human food.
10.2. Personalized Nutrition for Pets
Another trend is personalized nutrition for pets, with companies offering customized diets based on factors such as age, breed, activity level, and health conditions.
10.3. Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly Options
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is growing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly pet food options.
10.4. Technological Advancements in Manufacturing
Technological advancements in manufacturing are also playing a role in the pet food industry, with companies using new technologies to improve product quality, safety, and efficiency.
11. The Role of Pet Owners in Ensuring Safety
Pet owners play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of their pets and themselves when it comes to pet food.
11.1. Choosing Reputable Brands
It’s important to choose reputable brands that follow strict quality control procedures and use high-quality ingredients.
11.2. Reading Labels Carefully
Pet owners should read labels carefully to understand the ingredients and nutritional content of the food they are feeding their pets.
11.3. Following Feeding Guidelines
Following feeding guidelines is essential for ensuring that pets receive the right amount of nutrition.
11.4. Monitoring Pet Health
Pet owners should monitor their pet’s health and consult with a veterinarian if they notice any changes in appetite, behavior, or physical condition.
12. Legal and Ethical Implications
The question of whether humans can eat fresh pet food also raises legal and ethical implications.
12.1. Liability Issues
Pet food companies could face liability issues if humans are harmed by consuming their products.
12.2. Transparency and Disclosure
Pet food companies have a responsibility to be transparent and disclose all relevant information about their products, including potential risks associated with human consumption.
12.3. Consumer Rights
Consumers have the right to accurate and informative labeling, as well as the right to seek legal recourse if they are harmed by a product.
12.4. Ethical Considerations for Pet Food Companies
Pet food companies should consider the ethical implications of their marketing practices and product formulations, and prioritize the safety and well-being of both pets and humans.
13. Further Research and Resources
For those interested in learning more about pet food safety and regulations, here are some further research and resources:
13.1. Government Agencies
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA)
13.2. Industry Organizations
- Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO)
- Pet Food Institute (PFI)
13.3. Consumer Advocacy Groups
- Truth About Pet Food
- Association for Truth in Pet Food
13.4. Scientific Studies and Publications
- Journal of Food Protection
- Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association
14. Conclusion: Prioritizing Safety and Making Informed Choices
Ultimately, the decision of whether to consume pet food is a personal one. However, it’s important to prioritize safety and make informed choices based on the available evidence. At PETS.EDU.VN, we believe that pet food is formulated for animals and is best left to our furry friends. The potential health risks associated with human consumption outweigh any perceived benefits.
Remember, PETS.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the most up-to-date information and resources to help you make the best decisions for your pet’s health and well-being. If you have any further questions or concerns about pet food safety, don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
PETS.EDU.VN – Your trusted source for pet care information.
For more in-depth information and services, visit PETS.EDU.VN or contact us at 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-987-6543.
FAQ: Can Humans Eat Fresh Pet?
Here are 10 frequently asked questions about the safety of humans eating fresh pet food:
-
Is Freshpet safe for humans to eat?
No, Freshpet and other pet foods are not formulated or manufactured for human consumption and may pose health risks. -
What are the potential health risks of eating Freshpet?
Risks include bacterial contamination (Salmonella, E. coli), parasites, chemical contaminants, and nutritional imbalances. -
Are the ingredients in Freshpet human-grade?
Freshpet products are not human grade, they are not manufactured in a licensed human food facility. They are feed grade. -
What does “feed grade” mean?
“Feed grade” refers to ingredients and manufacturing processes that meet the minimum standards for animal feed but may not be suitable for human consumption. -
How do pet food regulations differ from human food regulations?
Pet food regulations are generally less stringent than those for human food, with fewer requirements for hygiene, sanitation, and ingredient quality. -
Can eating pet food cause food poisoning in humans?
Yes, pet food may contain harmful bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli, which can cause food poisoning in humans. -
Is it safe to feed pet food to children or elderly individuals?
No, it is not safe to feed pet food to children or elderly individuals due to the potential health risks. -
What should I do if I accidentally eat pet food?
Consult with a healthcare professional if you experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. -
Are there any situations where it’s acceptable for humans to eat pet food?
In emergency situations where human food is not available, consuming pet food may be considered as a last resort, but only after carefully weighing the potential risks and benefits. -
Where can I find more information about pet food safety?
Visit pets.edu.vn for reliable information and resources on pet food safety and regulations. You can also contact us at 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-987-6543.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and should not be considered a substitute for professional advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional or veterinarian for personalized recommendations.
