At PETS.EDU.VN, we understand your concerns about animal welfare. This article explores the facts surrounding PETA’s animal euthanasia practices, providing a balanced perspective on the issue. Learn about animal shelter statistics, ethical considerations, and responsible pet ownership.
1. Understanding PETA’s Animal Euthanasia Rates
People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA), a well-known animal rights organization, has faced scrutiny regarding the number of animals euthanized at its animal shelter in Norfolk, Virginia. Understanding the context of these numbers requires examining the data reported to the Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (VDACS).
1.1. Official Data on PETA’s Euthanasia Rates
As an animal shelter regulated by VDACS, PETA is required to submit annual reports detailing the animals it housed and their outcomes. These reports include the number of animals euthanized, adopted, and transferred to other facilities. Analyzing these reports over the years reveals consistently high euthanasia rates compared to other shelters in Virginia.
Table 1: Comparison of Euthanasia Rates in Virginia Shelters (2023)
| Shelter Type | Euthanasia Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| PETA | 73% |
| All Public Shelters | 11% |
| All Private Shelters | 8% |
| All Agencies Combined | 10% |
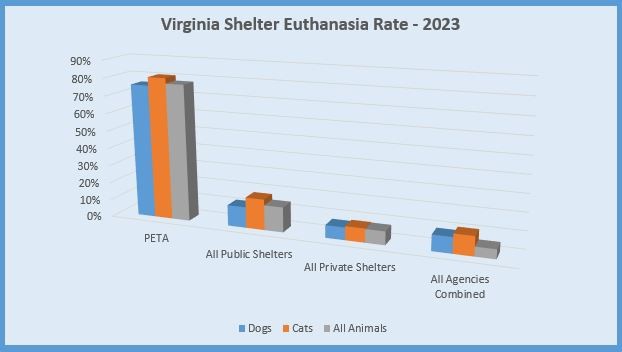
Source: Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (VDACS)
1.2. PETA’s Justification for Euthanasia
PETA defends its euthanasia practices by stating that it operates as an “open admission” shelter, accepting all animals regardless of their health or temperament. They argue that many animals they receive are severely ill, injured, or aggressive, making them unadoptable and necessitating euthanasia as a humane option. They also assert that “no-kill” shelters have lower euthanasia rates because they selectively accept animals, turning away those with significant medical or behavioral issues.
1.3. Examining the “Open Admission” Argument
While PETA’s “open admission” policy is a factor, it doesn’t fully explain the disparity in euthanasia rates. The Norfolk Animal Care Center (NACC), also an open admission shelter in the same city, reports significantly lower euthanasia rates. This suggests that factors beyond open admission, such as adoption efforts, resources, and shelter policies, play a crucial role.
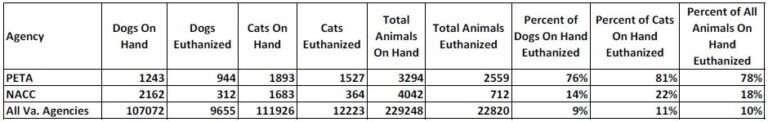
Table 2: Comparison of PETA and NACC Euthanasia Rates (2023)
| Animal Type | Shelter | Intake | Euthanized | Euthanasia Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dogs | PETA | 541 | 411 | 76% |
| NACC | 920 | 129 | 14% | |
| Cats | PETA | 654 | 478 | 73% |
| NACC | 783 | 102 | 13% | |
| Other | PETA | 152 | 111 | 73% |
| NACC | 39 | 4 | 10% |
Source: Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (VDACS)
1.4. The Debate on “Good Death” (Euthanasia)
PETA often describes euthanasia as a “good death,” arguing that it’s a compassionate way to end the suffering of animals with no hope of recovery or adoption. However, this view is controversial. Critics argue that PETA’s high euthanasia rates indicate a lack of effort in finding alternatives, such as rehabilitation, foster care, or adoption programs.
1.5. Factors Contributing to Euthanasia Decisions
Euthanasia decisions are complex and involve various factors:
- Animal’s Health: Severe illness, injury, or incurable conditions.
- Temperament: Aggression, fearfulness, or behavioral issues that pose a safety risk.
- Resources: Shelter capacity, funding for medical care and rehabilitation, and staff availability.
- Adoption Prospects: The likelihood of finding a suitable home for the animal.
- Legal Considerations: State and local laws regarding animal care and euthanasia.
2. Examining Animal Shelter Ethics and Responsibilities
The high euthanasia rates at PETA’s shelter raise fundamental questions about the ethics and responsibilities of animal shelters. Balancing animal welfare with limited resources is a constant challenge for shelters worldwide.
2.1. The “No-Kill” Movement and its Impact
The “no-kill” movement advocates for reducing euthanasia rates to a minimum, aiming to save all healthy and treatable animals. No-kill shelters prioritize adoption, foster care, and rehabilitation programs to find homes for as many animals as possible. This movement has significantly influenced shelter practices and public perception of animal euthanasia.
2.2. Challenges Faced by Open Admission Shelters
Open admission shelters face unique challenges, including:
- Overcrowding: Accepting all animals can lead to overcrowding, straining resources and increasing stress for animals.
- High Medical Costs: Treating sick and injured animals can be expensive, depleting funds for other programs.
- Behavioral Issues: Dealing with aggressive or fearful animals requires specialized training and resources.
- Public Perception: Open admission shelters may face criticism for high euthanasia rates, even when they are making difficult decisions in the best interest of the animals.
2.3. The Importance of Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are crucial for animal shelters. Shelters should openly report their intake, adoption, and euthanasia statistics, allowing the public to assess their performance. Independent audits and oversight can help ensure that shelters are adhering to ethical standards and best practices.
2.4. Comparing Euthanasia Rates Across Shelters
Comparing euthanasia rates across shelters requires careful consideration of factors such as:
- Admission Policies: Open admission vs. selective admission.
- Service Area: Rural vs. urban, which can affect the types of animals received.
- Community Resources: Availability of veterinary care, spay/neuter programs, and adoption services.
- Data Reporting Methods: Consistent and accurate data collection is essential for meaningful comparisons.
2.5. The Role of Community Support in Reducing Euthanasia
Community support is vital for reducing euthanasia rates. This includes:
- Adopting from Shelters: Providing homes for adoptable animals.
- Fostering Animals: Providing temporary care for animals in need.
- Volunteering at Shelters: Assisting with animal care, adoption events, and fundraising.
- Donating to Shelters: Providing financial support for medical care, food, and other essential resources.
- Supporting Spay/Neuter Programs: Preventing pet overpopulation.
3. Debunking Misconceptions about Animal Euthanasia
Misconceptions about animal euthanasia can fuel strong emotions and misinformed opinions. Clarifying these misconceptions is essential for fostering a more rational and compassionate discussion.
3.1. Myth: Euthanasia is Always Unnecessary
While every effort should be made to save animal lives, euthanasia is sometimes the most humane option. Animals suffering from severe, untreatable conditions may experience chronic pain and distress. Euthanasia can provide relief and prevent prolonged suffering.
3.2. Myth: “No-Kill” Shelters Never Euthanize
“No-kill” shelters euthanize animals in cases of severe illness, injury, or aggression that pose a significant threat to public safety. The goal is to minimize euthanasia, not eliminate it entirely.
3.3. Myth: Euthanasia is a Quick and Easy Solution
Euthanasia decisions are never taken lightly. Shelter staff often experience emotional distress when euthanizing animals, even when it is the most compassionate choice.
3.4. Myth: All Shelters Have the Same Resources
Animal shelters vary significantly in their resources, including funding, staff, and facilities. Comparing euthanasia rates without considering these disparities can be misleading.
3.5. Myth: Euthanasia Rates are the Only Measure of a Shelter’s Success
Euthanasia rates are just one metric for evaluating a shelter’s performance. Other important factors include adoption rates, animal care standards, community outreach programs, and efforts to prevent animal cruelty.
4. Responsible Pet Ownership and Reducing Animal Euthanasia
Responsible pet ownership plays a crucial role in reducing animal euthanasia rates. By making informed decisions and providing proper care, pet owners can help prevent animal suffering and overcrowding in shelters.
4.1. The Importance of Spaying and Neutering
Spaying and neutering are essential for preventing pet overpopulation. Millions of unwanted animals end up in shelters each year, many of whom are euthanized due to lack of space and resources. Spaying and neutering also offer health benefits for pets, such as reducing the risk of certain cancers.
4.2. Choosing the Right Pet for Your Lifestyle
Before acquiring a pet, carefully consider your lifestyle, resources, and ability to provide proper care. Research different breeds and species to find a pet that is a good fit for your home and family.
4.3. Providing Proper Care and Training
Pets require proper care, including:
- Nutrition: A balanced diet appropriate for their age, breed, and activity level.
- Veterinary Care: Regular checkups, vaccinations, and preventative care.
- Exercise: Daily physical activity to maintain their health and well-being.
- Mental Stimulation: Enrichment activities to prevent boredom and behavioral problems.
- Training: Basic obedience training to ensure they are well-behaved and safe.
- Socialization: Exposure to different people, animals, and environments.
4.4. Preventing Pet Abandonment
Pet abandonment is a major contributor to shelter overcrowding. If you are no longer able to care for your pet, explore all possible alternatives before surrendering them to a shelter. This includes:
- Finding a new home: Reach out to friends, family, and online pet adoption communities.
- Working with a rescue organization: Rescue groups specialize in finding homes for specific breeds or types of animals.
- Seeking temporary assistance: Some organizations offer temporary pet care assistance for owners facing financial or personal hardships.
4.5. Supporting Animal Welfare Organizations
Supporting animal welfare organizations helps them provide care for animals in need, promote responsible pet ownership, and advocate for stronger animal protection laws.
5. Examining PETA’s Broader Impact on Animal Welfare
While PETA’s euthanasia practices are controversial, the organization has also made significant contributions to animal welfare through its advocacy and activism. Evaluating PETA’s overall impact requires considering both its positive and negative aspects.
5.1. PETA’s Advocacy for Animal Rights
PETA has been a vocal advocate for animal rights, raising awareness about issues such as:
- Factory Farming: PETA has exposed the cruel conditions in factory farms and promoted veganism as an ethical alternative.
- Animal Testing: PETA has campaigned against animal testing for cosmetics, household products, and medical research.
- Entertainment: PETA has protested the use of animals in circuses, zoos, and marine parks.
- The Fur Industry: PETA has worked to end the fur trade by educating consumers about the cruelty involved in fur production.
5.2. PETA’s Educational Campaigns
PETA has launched numerous educational campaigns to promote animal welfare, including:
- Veganism: PETA promotes veganism as a way to reduce animal suffering and improve human health.
- Animal Cruelty Awareness: PETA educates the public about the signs of animal cruelty and how to report it.
- Responsible Pet Ownership: PETA provides information on spaying/neutering, proper pet care, and adoption.
5.3. PETA’s Rescue Efforts
PETA has conducted rescue operations to save animals from abusive situations, including:
- Factory Farms: PETA has rescued animals from factory farms and provided them with sanctuary.
- Laboratories: PETA has rescued animals from laboratories and found them loving homes.
- Neglectful Owners: PETA has rescued animals from owners who were neglecting or abusing them.
5.4. Criticisms of PETA’s Tactics
PETA’s tactics have been criticized for being:
- Sensationalistic: PETA’s campaigns often use graphic imagery and provocative language to shock and offend.
- Misleading: PETA has been accused of exaggerating or misrepresenting facts to promote its agenda.
- Counterproductive: Some critics argue that PETA’s extreme tactics alienate potential supporters and undermine the animal rights movement.
5.5. Evaluating PETA’s Overall Impact
Evaluating PETA’s overall impact on animal welfare is complex and subjective. While the organization’s euthanasia practices are concerning, its advocacy and educational efforts have raised awareness about animal rights and inspired positive change.
6. Alternative Solutions to Animal Euthanasia
Exploring alternative solutions to animal euthanasia is essential for improving animal welfare and reducing the number of animals euthanized in shelters.
6.1. Enhanced Adoption Programs
Enhanced adoption programs can increase the number of animals finding homes:
- Adoption Events: Hosting adoption events at local businesses and community centers.
- Online Pet Adoption Platforms: Utilizing online platforms to showcase adoptable animals.
- Reduced Adoption Fees: Offering reduced adoption fees to incentivize adoption.
- Adoption Counseling: Providing counseling to help adopters choose the right pet for their lifestyle.
- Post-Adoption Support: Offering post-adoption support to help adopters address any challenges they may face.
6.2. Foster Care Programs
Foster care programs provide temporary homes for animals in need:
- Medical Foster Care: Providing care for animals recovering from illness or injury.
- Behavioral Foster Care: Providing training and socialization for animals with behavioral issues.
- Puppy/Kitten Foster Care: Providing care for orphaned puppies and kittens.
- Senior Foster Care: Providing care for senior animals who may have difficulty finding permanent homes.
6.3. Targeted Spay/Neuter Programs
Targeted spay/neuter programs can reduce pet overpopulation in specific areas:
- Mobile Spay/Neuter Clinics: Providing low-cost spay/neuter services in underserved communities.
- Community Cat Programs: Trapping, neutering, and returning (TNR) feral cats to their colonies.
- Incentive Programs: Offering incentives for pet owners to spay/neuter their pets.
6.4. Shelter Enrichment Programs
Shelter enrichment programs can improve the quality of life for animals in shelters:
- Playtime: Providing opportunities for animals to play and socialize.
- Puzzle Toys: Providing puzzle toys to stimulate their minds.
- Comfort Items: Providing comfortable bedding and toys.
- Human Interaction: Providing regular interaction with shelter staff and volunteers.
6.5. Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration and partnerships between animal shelters, rescue organizations, and veterinary clinics can maximize resources and improve outcomes for animals.
7. How to Support Ethical Animal Shelters and Organizations
Supporting ethical animal shelters and organizations is a crucial step in promoting animal welfare and reducing animal euthanasia.
7.1. Researching Shelters and Organizations
Before supporting a shelter or organization, research its mission, policies, and practices. Look for shelters that:
- Have transparent data reporting: They openly report their intake, adoption, and euthanasia statistics.
- Prioritize adoption and foster care: They actively promote adoption and have robust foster care programs.
- Have high standards of animal care: They provide proper medical care, nutrition, and enrichment for their animals.
- Are financially responsible: They use their funds wisely and have a clear fundraising strategy.
7.2. Volunteering Your Time
Volunteering your time at an animal shelter can make a significant difference in the lives of animals:
- Animal Care: Assisting with feeding, cleaning, and grooming.
- Adoption Events: Helping with adoption events and showcasing adoptable animals.
- Fundraising: Assisting with fundraising efforts.
- Administrative Tasks: Helping with administrative tasks such as answering phones and filing paperwork.
7.3. Donating Money and Supplies
Donating money and supplies helps shelters provide care for animals in need:
- Monetary Donations: Providing financial support for medical care, food, and other essential resources.
- Supply Donations: Donating items such as food, bedding, toys, and cleaning supplies.
7.4. Fostering Animals
Fostering animals provides them with a temporary home and helps them prepare for adoption:
- Providing a loving home: Giving animals a safe and comfortable environment.
- Socializing animals: Exposing animals to different people, animals, and environments.
- Providing medical care: Administering medications and taking animals to veterinary appointments.
7.5. Advocating for Animal Welfare
Advocating for animal welfare can help create a more compassionate and just world for animals:
- Supporting animal protection laws: Contacting your elected officials and urging them to support animal protection laws.
- Educating others about animal welfare: Sharing information about animal welfare issues with your friends, family, and community.
- Adopting a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle: Reducing your consumption of animal products to reduce animal suffering.
8. Understanding the Legal Framework Surrounding Animal Euthanasia
The legal framework surrounding animal euthanasia varies by state and locality. Understanding these laws is essential for ensuring that euthanasia is performed humanely and ethically.
8.1. State Laws on Animal Euthanasia
State laws typically regulate:
- Who can perform euthanasia: Only licensed veterinarians or certified euthanasia technicians may be authorized to perform euthanasia.
- Acceptable methods of euthanasia: Acceptable methods of euthanasia are typically defined by the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA).
- Record-keeping requirements: Shelters and veterinarians may be required to keep records of all animals euthanized.
8.2. Local Ordinances on Animal Euthanasia
Local ordinances may impose additional regulations on animal euthanasia, such as:
- Restrictions on the use of certain euthanasia methods: Some localities may restrict the use of certain euthanasia methods, such as gas chambers.
- Requirements for training and certification of euthanasia technicians: Local ordinances may require euthanasia technicians to undergo specific training and certification.
- Regulations on the disposal of euthanized animals: Local ordinances may regulate the disposal of euthanized animals to prevent the spread of disease.
8.3. The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) Guidelines
The AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals are widely recognized as the gold standard for humane euthanasia. These guidelines provide detailed recommendations on acceptable methods of euthanasia for different species of animals.
8.4. Ensuring Compliance with Legal Requirements
Animal shelters and veterinary clinics must ensure that they are in compliance with all applicable state and local laws regarding animal euthanasia. This includes:
- Using only approved methods of euthanasia: Adhering to the AVMA Guidelines and state and local laws.
- Properly training and certifying euthanasia technicians: Ensuring that euthanasia technicians are properly trained and certified.
- Maintaining accurate records: Keeping detailed records of all animals euthanized.
8.5. Reporting Animal Cruelty and Illegal Euthanasia
If you suspect animal cruelty or illegal euthanasia, report it to your local animal control agency or law enforcement.
9. The Future of Animal Sheltering and Euthanasia
The future of animal sheltering and euthanasia depends on a collective effort to promote responsible pet ownership, support ethical shelters, and advocate for stronger animal protection laws.
9.1. Advancements in Veterinary Medicine
Advancements in veterinary medicine are improving the health and well-being of animals, reducing the need for euthanasia:
- New Treatments for Diseases: New treatments are being developed for diseases that were once considered incurable.
- Improved Pain Management Techniques: Improved pain management techniques are helping to alleviate suffering in animals.
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures: Minimally invasive surgical procedures are reducing the recovery time and pain associated with surgery.
9.2. Increased Public Awareness of Animal Welfare
Increased public awareness of animal welfare is leading to more responsible pet ownership:
- More people are adopting from shelters: Adoption rates are increasing as more people become aware of the importance of adopting from shelters.
- More people are spaying and neutering their pets: Spay/neuter rates are increasing as more people become aware of the benefits of spaying and neutering.
- More people are supporting animal welfare organizations: Donations to animal welfare organizations are increasing as more people become aware of the importance of supporting these organizations.
9.3. Technological Innovations in Animal Sheltering
Technological innovations are improving the efficiency and effectiveness of animal sheltering:
- Shelter Management Software: Shelter management software is helping shelters to track their inventory, manage their finances, and communicate with adopters and fosters.
- Microchipping: Microchipping is helping to reunite lost pets with their owners.
- DNA Testing: DNA testing is helping to identify the breeds of mixed-breed dogs, which can help adopters choose the right pet for their lifestyle.
9.4. The Role of Data Analytics in Reducing Euthanasia
Data analytics can be used to identify trends and patterns in animal sheltering, which can help shelters to:
- Target their adoption efforts: Identify the types of animals that are most likely to be adopted.
- Improve their spay/neuter programs: Identify the areas where pet overpopulation is most prevalent.
- Optimize their resource allocation: Allocate resources to the programs that are most effective in reducing euthanasia.
9.5. A Vision for a More Humane Future
A vision for a more humane future includes:
- Every animal has a loving home: All adoptable animals find loving homes.
- Pet overpopulation is eliminated: Spay/neuter rates are high enough to prevent pet overpopulation.
- Animal cruelty is eradicated: All animals are treated with respect and compassion.
- Euthanasia is only used as a last resort: Euthanasia is only used to relieve suffering in animals with no hope of recovery.
10. Conclusion: Finding Resources and Support at PETS.EDU.VN
Understanding the complexities surrounding animal euthanasia, especially concerning organizations like PETA, requires a balanced perspective. While PETA’s high euthanasia rates are a cause for concern, it’s essential to consider their broader contributions to animal welfare and the challenging circumstances faced by open-admission shelters. Responsible pet ownership, supporting ethical animal shelters, and advocating for stronger animal protection laws are crucial steps toward a more humane future for all animals.
At PETS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with comprehensive information and resources to help you make informed decisions about pet care and animal welfare. Explore our website for in-depth articles on responsible pet ownership, ethical animal shelters, and alternative solutions to animal euthanasia. Contact us at 789 Paw Lane, Petville, CA 91234, United States, Whatsapp: +1 555-987-6543, or visit our website at PETS.EDU.VN to learn more and connect with our community of pet lovers. Your journey toward compassionate pet ownership starts here! Discover expert advice on animal rescue and ethical treatment, fostering a world where every pet thrives.
FAQ: Understanding Animal Euthanasia and PETA’s Role
- What is animal euthanasia? Animal euthanasia is the humane killing of an animal to relieve suffering.
- Why is euthanasia performed in animal shelters? Euthanasia is performed when an animal is severely ill, injured, or has behavioral issues that make them unadoptable.
- What is PETA’s stance on euthanasia? PETA believes euthanasia is sometimes necessary to prevent animal suffering, particularly in open-admission shelters.
- Why is PETA’s euthanasia rate controversial? PETA’s euthanasia rate is high compared to other shelters, raising concerns about their efforts to find alternatives.
- What is an open-admission shelter? An open-admission shelter accepts all animals, regardless of health or temperament.
- What is a no-kill shelter? A no-kill shelter aims to save all healthy and treatable animals, minimizing euthanasia.
- How can I support ethical animal shelters? Support shelters that prioritize adoption, have transparent data, and high standards of animal care.
- What can I do to reduce animal euthanasia? Spay/neuter your pets, adopt from shelters, and support animal welfare organizations.
- What are the alternatives to euthanasia? Alternatives include adoption, foster care, rehabilitation, and sanctuary programs.
- Where can I find more information about animal welfare? Visit pets.edu.vn for comprehensive resources and support on all aspects of pet care and animal welfare.
